Cold Plates
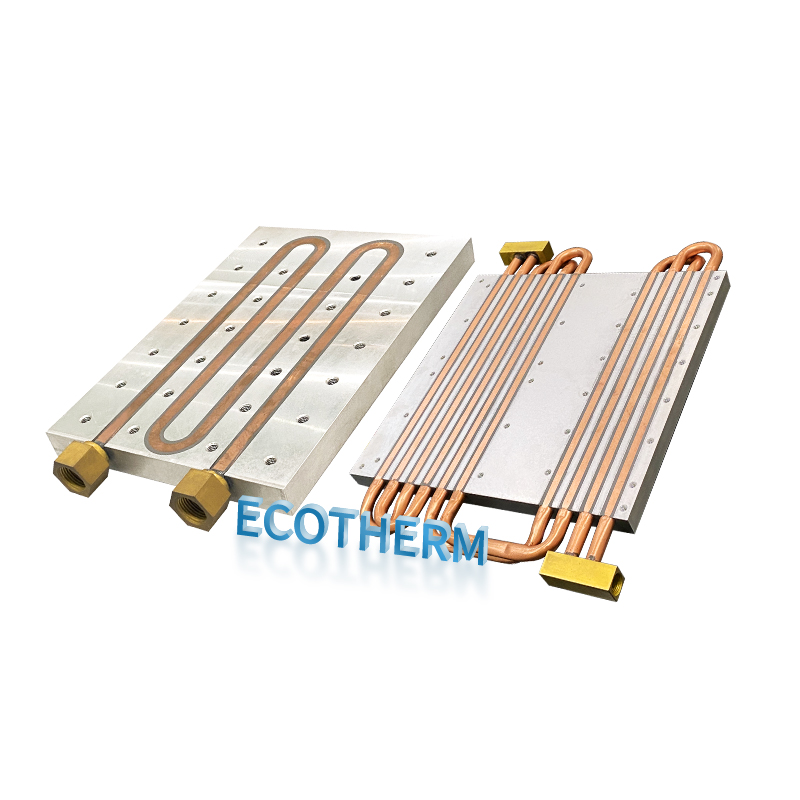

Cold Plates help you control heat in powerful machines. You use them to keep electronics, cars, and energy systems cool. Their design lets liquid flow through channels, moving heat away fast. The latest models reach heat transfer rates from 100 to 20,000 W/m²·K, much higher than air cooling.
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Liquid-cooled cold plates share | 68% |
Heat transfer coefficient (liquid) | 100-20,000 W/m²·K |
Heat transfer coefficient (air) | 25-250 W/m²·K |
You see cold plate technology growing in AI, electric vehicles, and data centers. This means your devices run better and last longer.
Key Takeaways
Cold Plates cool electronics, cars, and energy systems very well. This helps them work better and last longer. – Pick the best material for your needs. Use aluminum if you want it light. Use copper if you need better heat transfer. This makes cooling work better. – Take care of Cold Plates often. Check the coolant levels. This can help your equipment last much longer. – Think about how the coolant channels are made. Good flow stops hot spots. It also spreads heat evenly. – Using liquid cooling with Cold Plates can lower energy bills. It can also cut down on greenhouse gas emissions. This makes it better for the environment.
How Cold Plates Work
Heat Transfer Principle
You can learn about Cold Plates by seeing how they move heat. These devices use two main ways to transfer heat. One way is conduction. The other way is convection.
The metal plate touches the hot part. Heat moves through the plate by conduction.
A cooling fluid flows inside the plate’s channels. This fluid takes heat from the plate’s surface.
The fluid then carries the heat away. It goes to another place, like a heat exchanger.
There is science behind this process. Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction explains how heat moves in a solid. The law uses this formula:
Q = -k A ΔT / d
Where:
k means how well the plate material moves heat,
A is the area where heat travels,
ΔT is the temperature difference between the hot part and the cooling fluid,
d is the thickness of the plate.
When you use a Cold Plate, you want the material to move heat fast. This helps heat go quickly from the hot part to the fluid. The cooling fluid then takes the heat away. This keeps your equipment safe.
Key Components
Every Cold Plate has important parts. Each part helps the plate work better and keeps things cool.
Base Plate Material: Most Cold Plates use aluminum or copper. Aluminum is light and does not rust. Copper moves heat faster and keeps the plate’s temperature even.
Coolant Channels: These are small paths inside the plate. The coolant flows through these channels and picks up heat.
Inlet and Outlet Ports: These let the coolant go in and out. Good design helps the fluid flow smoothly and keeps the temperature even.
Internal Structures: Some plates have fins or special shapes inside. These help spread heat and keep the temperature steady.
Here is a table showing the main materials used in Cold Plates:
Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
Aluminum | ~205 | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, cost-effective |
Copper | ~400 | Superior thermal conductivity, excellent temperature uniformity |
Stainless Steel | N/A | Exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength |
How the coolant flows inside the plate is very important. When the coolant moves evenly, it spreads heat out. This stops hot spots from forming. Your Cold Plate can handle more power and keep things safe. If you use more outlets, you get better heat distribution.
Other things also affect how well your Cold Plate works:
Factor | Influence on Performance |
|---|---|
Flow Rate | High uniform flow rate in channels keeps heat spread out. |
Temperature Differential | Plates with fins lose heat better and keep low pressure drop. |
Internal Structure Design | Fins help keep temperature even better than bars. |
You can see that flow rate, temperature difference, and inside design matter a lot. Radian’s Cold Plates use smart channel layouts and good materials like aluminum and copper. This helps you get the best cooling for your needs.
Tip: For the best results, pick a Cold Plate with a design that fits your cooling needs and uses the right material for your job.
Cold Plates Applications
Electronics Cooling
You use electronics all the time. Things like computers and servers need to stay cool. Cold Plates help keep these devices from getting too hot. They are used in data centers to move heat away fast and lower pressure. In telecom equipment, Cold Plates protect parts in small spaces. Radian’s Cold Plates cool power electronics, CPUs, and GPUs. This stops them from overheating and helps them last longer.
Application Area | Performance Improvements |
|---|---|
Data Centers | Better heat transfer and less pressure. |
Telecommunications | Safe use in tight, hot places. |
6G Telecom Hardware | Helps keep temperature and signals steady. |
You get better energy use and higher efficiency. Liquid cooling lets you build more compact systems. You can also add more devices easily. This saves power and cuts costs.
Aerospace and Automotive
Cold Plates are used in planes and cars. In planes, they keep avionics and power systems cool. In cars, they cool engines and electric vehicle batteries. You also find them in lasers, fuel cells, and motor drives. Cold Plates keep temperatures steady. This is important for safety and good performance.
Used in car engine cooling
Used in avionics cooling
Used in nuclear reactor cooling
Used in lasers and battery coolers
Used in motor drives and medical gear
Cold Plates stop overheating and hot spots. They help make systems lighter and smaller. This matters for fast cars and planes. You get longer battery life and safer electric vehicles.
Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
Good thermal management | Keeps battery cells at the same temperature. |
Lower risk of thermal events | Makes dangerous heat problems less likely. |
Longer battery life | Slows battery aging, so you get more charges. |
Stops hot spots | Spreads heat out, making things safer. |
Better efficiency | Makes vehicles work better and batteries last longer. |
Renewable Energy
Cold Plates are used in solar farms and wind turbines. They keep inverter modules and rectifiers cool, even when making lots of energy. This protects electronics and helps them last longer.
Source | Evidence |
|---|---|
Kenfa Tech | Cold plates are attached to inverter modules and rectifiers to keep them safe, even when making lots of energy. They are part of the cooling system in solar farms and wind turbines. |
Cold Plates keep solar inverters and wind turbine electronics at the right temperature.
They protect important parts, so you get steady power and longer equipment life.
You get energy systems that work well and last a long time. Cold Plates help your renewable energy gear stay safe and run for years.
Tip: If you pick Cold Plates for your system, you make it more reliable and better for tough jobs.
Types of Cold Plates
Liquid Cold Plates
Liquid cold plates help cool strong devices. Coolant moves through channels inside the plate. This takes heat away from the device. There are many kinds of liquid cold plates. Each kind has its own design and use. Look at this table to see how each type works and where you use it:
Type of Cold Plate | Performance Characteristics | Suitable Applications | |
|---|---|---|---|
Embedded Tube Cold Plates | Metal base with tubes for coolant flow. | Higher thermal resistance, moderate cooling. | Moderate cooling needs. |
Brazed Cold Plates | Thin metal sheets stacked with complex channels. | High thermal performance, short conduction path. | Power electronics, high-performance systems. |
Extruded Cold Plates | Extruded metal with built-in channels. | Good thermal conductivity, lower cost. | Servers, medium-demand cooling. |
Bonded Fin Cold Plates | Base plate with fins attached for more surface area. | Better cooling efficiency. | Power electronics, renewable energy. |
Hybrid Cold Plates | Mix of different cooling technologies. | Versatile, customizable, strong performance. | Unique cooling needs. |
Microchannel Cold Plates | Tiny channels for coolant, large surface area. | Excellent cooling performance. | Lasers, high-power devices. |
Composite Cold Plates | Mix of metals and non-metals for light weight. | Superior thermal conductivity, strong build. | Aerospace, military. |
Liquid cold plates cool better than air. Liquids soak up heat fast and move it away. This keeps temperatures steady and makes less noise. You can make small systems that use lots of power.
Tip: You can get custom designs for your needs. Radian lets you pick straight, winding, or tiny channel layouts. You choose the material, channel shape, and how to mount it.
Machined, Bonded, Brazed Designs
You can pick how your cold plate is made. Each way changes how well it cools and how much it costs.
Brazed cold plates use thin sheets and special fins. They cool best because they have low resistance and lots of surface.
Deep-machined plates let you shape the channels. You can make the coolant go right to hot spots.
Friction Stir Welded cold plates are very strong. You use them when you need no leaks and high pressure.
There are other choices too:
Vacuum brazed cold plates seal tight and work for tricky shapes.
Tube embedded heat sinks cost less and cool okay.
Die cast liquid cold plates are light and good for gadgets.
Extruded liquid cooling heat sinks are used in factories.
Gun drilled cold plates make exact coolant paths.
How you make the plate changes cost and how it works. Extrusion and casting are for big orders. Machining lets you add holes, but costs more. The plate must be flat to cool well. If it is not flat, heat does not move right.
Note: You can work with Radian to pick the best way. You choose the material, channel shape, and features for your job.
Passive vs. Active Cooling
Cold plates can use passive or active cooling. Each type is good for different jobs. This table helps you compare them:
Feature | Passive Cooling | Active Cooling |
|---|---|---|
Advantages | Simple, no noise, less maintenance | High cooling power, temperature control, scalable |
Disadvantages | Limited cooling, needs more space, less control | More complex, noise, uses power |
Preferred Scenarios | Small systems, easy conditions | Critical jobs, high heat spikes |
Passive cooling uses air or heat spreaders. You do not need pumps or fans. Use passive plates in small or cool places. Active cooling uses pumps to move coolant. Use active plates in big or hot systems.
Tip: Pick passive cooling for easy jobs. Pick active cooling for hard jobs that need strong control.
There are many kinds of cold plates. You choose the design, material, and cooling type for your needs. Radian helps you change every part, like the channel shape or mounting holes. You get the best cooling for your job.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Efficiency and Reliability
You want your cooling system to work well for years. Radian’s designs help you get good efficiency and strong reliability. Here are some reasons:
Liquids move heat better than air. This means cooling is faster and works better.
You save space and weight. You do not need big fans or heat sinks.
Closed-loop systems keep cooling steady. They work well even when it gets very hot or cold.
New ways to make cold plates, like friction stir welding and vacuum brazing, make strong joints that do not leak.
Tube embedding lets you fit strong cooling in small spaces.
Lower costs make these systems a smart pick for many industries.
Cold plate technology helps the environment too. If you switch from air cooling to cold plates, you can lower greenhouse gas emissions by about 15%. You use less energy and water, which is better for the planet.
Cooling System | Cost Range |
|---|---|
Air Cooling | $20–100 |
AIOs | $80–200+ |
Custom Loops | $300–1,000+ |
Cooling System Type | Average Lifespan (Years) |
|---|---|
Liquid Cold Plate | 7 to 15 |
Air Cooling Systems | Shorter than liquid plates |
Maintenance and Limitations
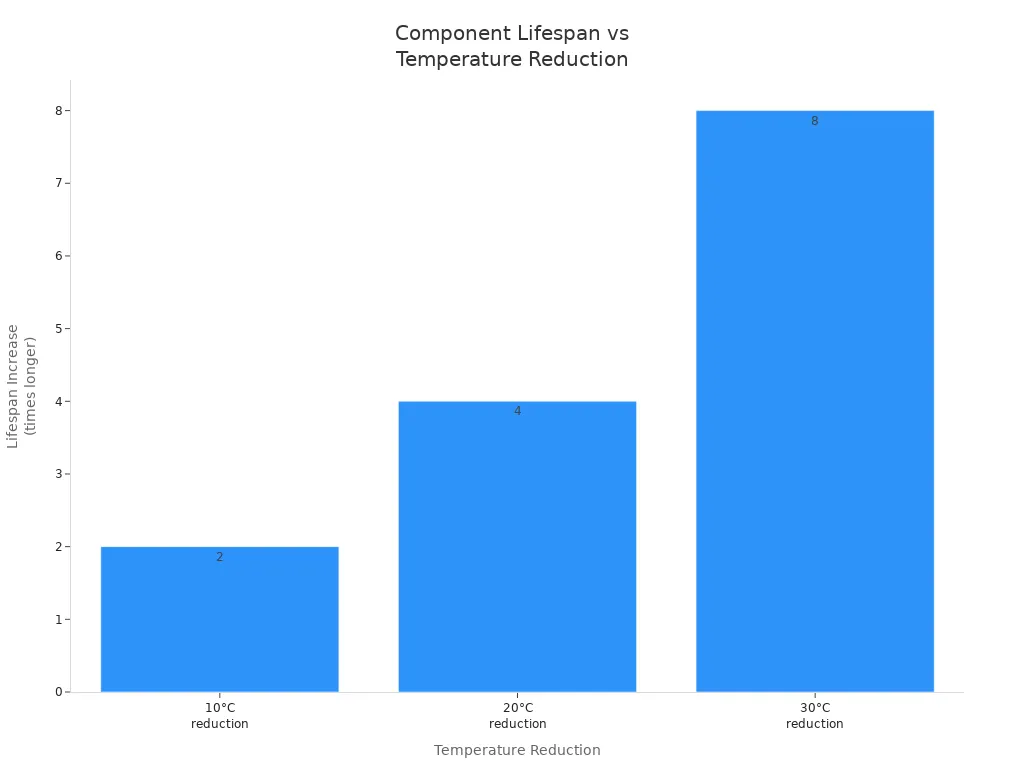
You need to care for your cooling system to keep it working well. Regular checks and cleaning help stop problems. If you lower the temperature by 10°C, your parts can last twice as long. If you lower it by 20°C, they can last four times longer. Look at this chart to see how cooler parts last longer:
“The number one cause of liquid cooling system failure is not doing maintenance. Many failures blamed on ‘bad parts’ are really from not taking care of the coolant. This lets corrosion hurt how the system works.” – Anthony Ramirez, Service Director at Industrial Cooling Systems
You should check coolant levels and look for leaks. Clean the system when needed. This keeps your Cold Plates working well and helps your equipment last longer.
Selecting Cold Plates
Key Criteria
When you pick a cooling solution, it should fit your needs. You need to look at some important things before you decide. The table below shows what you should check:
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Thermal Resistance | Shows how well the cold plate takes heat away from your device. |
Fluid Channel Dimensions | Custom channels help heat move better, lowering resistance and making it work better. |
Materials | Copper and aluminum are best because they move heat fast and last long. |
Coolant Compatibility | The coolant must work with your system for the best results. |
Customization Options | Special designs can help you get better cooling for your job. |
Tip: You can talk to companies like Radian to get a cold plate that fits your needs. They let you pick channel shapes, materials, and how to mount it.
Application Fit
You should think about your job before you pick a cold plate. How much heat your system makes will help you choose. If your device gets very hot, you need a strong cold plate. Space is important too. If you have a small space, you need a plate that fits but still cools well.
Here are some tips to help you match cold plate features to your needs:
Pick the best material. Use aluminum if you want it light and cheap, or copper if you want better heat movement.
Make the inside channels work well. Use straight channels for easy flow or winding ones for more heat pickup.
Make sure it lasts long and saves money. Add coatings to stop rust, use thermal models, and make sure it is easy to build.
You can work with experts to get a cold plate that fits your system. Radian helps you find the right one for your electronics, cars, or energy systems. When you pick the right cold plate, your equipment stays safe and works better.
Cold Plates help cool strong machines much better. They can make things up to 30% cooler. This helps electronics last twice as long. You also save money because you do not need big air conditioners.
Impact | Description |
|---|---|
Efficiency | Cold Plates cool up to 30% more than air. |
Reliability | Electronics last two times longer. |
Cost-Effectiveness | You spend less on air conditioning. |
Experts say liquid cooling works best for hard jobs. If you pick advanced Cold Plates like Radian’s, you get special designs. They work well and keep things safe anywhere.
FAQ
What is a cold plate?
A cold plate is a metal plate with channels inside. Coolant flows through these channels. The plate takes heat away from hot parts, like electronics or batteries. You use cold plates to keep your devices cool and safe.
How do I choose the right cold plate?
You should look at your device’s heat output, space, and cooling needs. Pick the right material, like aluminum or copper. You can ask experts at Radian for help. They can design a cold plate that fits your system.
Can I use cold plates in electric vehicles?
Yes, you can use cold plates in electric vehicles. They help keep batteries and power electronics cool. This makes your car safer and helps the battery last longer.
How often should I maintain my cold plate system?
You should check your cold plate system every few months. Look for leaks and make sure the coolant is clean. Regular checks help your system last longer and work better.
What are the main benefits of liquid cold plates?
Liquid cold plates move heat away quickly. You get better cooling than with air. Your devices run cooler and last longer. You also save space and energy.




