About Anodized Aluminum Heatsinks

You need good ways to keep your devices cool and safe. An anodized aluminum heat sink helps by moving heat away from important parts. The anodization process makes these heat sinks strong and trustworthy. It makes them resist rust, have a harder surface, stop electricity from passing through, and give off heat better.
| Surface Treatment | Emissivity Rating | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Bare Aluminum | 0.04-0.06 | Poor |
| Anodizing (Black) | 0.9+ | Very Good |
When you use anodization, your heat sink lasts longer and works better, even when things get tough.
Key Takeaways
- Anodized aluminum heat sinks help cool electronics. They move heat away from hot parts into the air.
- The anodization process makes them stronger. It stops rust, scratches, and damage. This helps them last a long time.
- Aluminum is used for heat sinks because it is light. It also moves heat very well. It works better than heavy materials like copper in many cases.
- Picking the right anodizing type is important. Type II looks nice. Type III is very strong. The type you choose can change how well the heat sink works and how long it lasts.
- Anodized surfaces let out heat better than non-anodized ones. This is important to keep devices working well.
- The size and shape of a heat sink matter a lot. Bigger areas and shapes like fins help get rid of heat and cool things down better.
- Good airflow around the heat sink is needed for best cooling. Make sure nothing blocks the air from moving.
- Cleaning anodized heat sinks is simple. Doing this often keeps them looking good and working well.
What Is an Anodized Aluminum Heat Sink
Basic Function and Role
An anodized aluminum heat sink helps keep electronics cool. It pulls heat away from hot parts and sends it into the air. This keeps devices from getting too hot. When you use a heat sink, your electronics last longer and work better.
- Anodized aluminum heat sinks move heat without using power.
- They take heat from hot parts and send it to the air.
- These heat sinks stop devices from overheating.
- The anodized layer helps stop rust and lets heat escape faster, so your equipment lasts longer.
Tip: An anodized aluminum heat sink helps stop damage from too much heat and keeps your electronics working well.
Why Aluminum Is Preferred
People pick aluminum for heat sinks because it is light and works well. Aluminum moves heat away from devices quickly. It is much lighter than copper, so it is easy to use.
- Aluminum can move heat at about 205 W/m·K.
- Alloys like A6061 and A6063 move heat at about 167 W/m-K.
- Aluminum heat sinks weigh half as much as copper ones.
- Copper moves heat better, but aluminum is cheaper and lighter.
Aluminum heat sinks are a smart and useful choice for many needs.
The Anodizing Process
Anodizing makes the surface of an aluminum heat sink stronger. This process uses electricity and a special bath to make a thick, tough layer on the aluminum. The heat sink can resist rust, wear less, and hold color dyes for a cool look.
| Step | Description | Impact on Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Cleaning | Cleans off dirt and grease with special cleaners. | Stops problems during anodizing. |
| Mechanical Finishing | Sands or polishes the surface to make it smooth. | Makes the finish even. |
| Masking | Covers parts that should not be anodized. | Protects only certain areas. |
| Anodizing Stage | Uses electricity in an acid bath to make the oxide layer. | Makes the surface hard and stops rust. |
| Sealing | Locks in the anodized layer and any color dyes. | Makes it last longer and protects it from the environment. |
An anodized aluminum heat sink looks nice and works well in tough places. The anodized layer helps it work better and look better, so it is a good choice for many uses.
Anodized Aluminum Heat Sink Benefits
Corrosion and Wear Resistance
If you pick an anodized aluminum heat sink, it can handle tough places. The anodization process puts a special layer on the aluminum. This layer keeps the heat sink safe from rust, scratches, and damage from things around it.
- The anodized layer works like a shield against water and chemicals.
- These heat sinks work in places where regular aluminum would not last.
- The surface gets much harder, so it does not scratch or dent easily.
Note: Anodized surfaces are much harder and do not wear out as fast as regular aluminum. This is important if your heat sink gets bumped or rubbed a lot.
Your anodized aluminum heat sink will last longer and keep working, even in rough places.
Electrical Isolation
Safety matters in every electronic device. Anodized aluminum heat sinks help keep your devices safe by stopping electricity from passing through. The anodized layer acts like an insulator.
Here is a quick look at how the anodized layer helps with electrical isolation:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Withstand Voltage | >500VDC |
| Surface Resistance | >5×10⁹ Ω |
You can use these heat sinks near important parts without worrying about short circuits. The anodized layer helps keep your electronics safe and working well.
Enhanced Emissivity
Heat sinks need to get rid of heat quickly. Anodized aluminum heat sinks do this better because the anodized surface lets out more heat. Emissivity shows how well a surface can send out heat as infrared energy.
Check out this comparison:
| Type of Heat Sink | Emissivity | Heat Dissipation Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Anodized Aluminum | ~0.05 | Reflects heat, does not cool well |
| Anodized Aluminum | ~0.85 | Sends out heat well, cools better |
| Overall Comparison | Anodized surfaces can send out up to 15 times more heat than bare aluminum |
If you use an anodized aluminum heat sink, it gets rid of heat better. This keeps your devices cooler and helps them last longer. The high emissivity of the anodized surface makes a big difference, especially if you use passive cooling.
Tip: For the best cooling, choose a heat sink with a high-emissivity anodized finish.
Surface Finish and Color
The finish and color of a heat sink are important. The finish changes how the heat sink looks and feels. It also affects how well it works. An anodized aluminum heat sink has a smooth and hard surface. This surface does not get damaged easily. The anodized layer lets you pick many colors. You can match your device or your brand.
There are different finishes and colors to choose from. Each one has its own good points for how it works and looks. Here is a table with the most common choices:
| Surface Finish/Color | Emissivity Impact | Application Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Clear Anodized | ~0.83 – 0.86 | Looks nice, costs less |
| Black Anodized | ~0.83 – 0.86 | Looks nice, gives a bit more heat radiation |
| Dyed Colors (e.g., Blue, Green) | ~0.83 – 0.86 | Looks nice, helps with branding |
| Hard-Coat Anodizing | Higher wear resistance | Good for tough places |
All anodized finishes help send out heat well. The emissivity stays high, between 0.83 and 0.86. This is true for every color you pick. Black anodized finishes may send out a little more heat. But all colors work well. You do not have to pick between looks and how well it works.
Picking a color helps with branding or telling devices apart. You can choose blue, green, or black for your company’s style. Clear anodized finishes look shiny and clean. Hard-coat anodizing is best for places that are rough or harsh.
Tip: The color of your heat sink does not change how well it cools. You can pick the color you like and not worry about performance.
A smooth and colored finish makes cleaning easy. Dust and dirt come off without much work. The finish does not scratch easily. Your heat sink will look new for a long time. An anodized aluminum heat sink gives you both style and good function.
Types of Anodizing
There are different types of anodizing for aluminum heat sinks. Each type gives special features to your heat sink. You can pick the best type for your needs.
Type II Anodizing
Type II anodizing makes a thin layer on the aluminum. The coating is about 0.7 to 1.2 mils thick. This process uses sulfuric acid. Type II anodizing gives a smooth and nice finish. It also helps stop rust.
Type II anodizing is used for parts that need to look good. It works well as a base for paint or powder coating. If you want a heat sink that looks nice and does not rust, Type II anodizing is a good choice.
Common uses for Type II anodizing:
- Makes parts look better
- Used as a base for other coatings
Tip: Pick Type II anodizing for a mix of looks and protection.
Type III Anodizing
Type III anodizing is also called hardcoat anodizing. It makes a much thicker and stronger layer. The coating is about 2.0 to 2.8 mils thick. This process uses chromic acid. You get great rust protection and high wear resistance. Type III anodizing costs more, but it makes your heat sink tough.
Type III anodizing is best for heat sinks in rough places. This includes machines, military gear, and aerospace parts. The thick layer keeps your heat sink safe from scratches, chemicals, and bad weather.
Where you use Type III anodizing:
- Used in factories
- Used in cars
- Used in military and aerospace
- Used in boats
Here is a table to help you choose:
| Property/Application | Type II Anodizing | Type III Anodizing |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Thickness | 0.7-1.2 mils (18-30 microns) | 2.0-2.8 mils (50-70 microns) |
| Primary Use | Looks, base for coatings | Tough places, strong protection |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Acid Used | Sulfuric acid | Chromic acid |
| Cost | Cheaper | Costs more |
Note: Type III anodizing is best for heat sinks in tough places.
Decorative Anodizing
Decorative anodizing is for color and looks. You can pick colors like blue, green, or black. This type gives a bright and even finish. It also helps stop rust and wear.
You might pick decorative anodizing to match your brand or make your heat sink stand out. The color does not change how well the heat sink works. You get both style and good function.
- Decorative anodizing is good for branding.
- It helps you tell devices apart by color.
- The finish stays bright and clean for a long time.
Tip: Decorative anodizing lets you pick colors without losing performance.
Now you know the main types of anodizing. You can choose the best one for your project and get great results for your heat sink.
Aluminum Alloys for Heat Sinks
Common Alloys (6061, 6063)
When you choose an aluminum heat sink, you often see two main alloys: 6061 and 6063. These alloys stand out because they offer strong thermal performance and good mechanical strength. You want your heat sink to move heat away from your device quickly. Both 6061 and 6063 can do this well.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Alloy | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|
| 6061 | 200 |
| 6063 | 200 |
6061 aluminum gives you high strength and flexibility. You use it when your project needs a heat sink that also supports weight or handles stress. This alloy works well in places where the heat sink must hold its shape and stay strong.
6063 aluminum offers a good mix of strength and thermal performance. You pick 6063 when you need a heat sink with a complex shape or fine details. This alloy is easy to extrude, so you can get creative with your designs. It works well for most cooling jobs in electronics, lighting, and power supplies.
Tip: Both 6061 and 6063 provide reliable heat transfer. You can trust them for most electronic cooling needs.
Alloy Selection by Application
You want the right alloy for your specific job. Each alloy brings something special to the table. Here is how you can match the alloy to your application:
- 6061-T6: Choose this alloy when you need structural strength. It works well for heat sinks that must support other parts or face mechanical stress.
- 6063-T5: Pick this alloy for complex extrusions. It is perfect for heat sinks with many fins or detailed shapes.
- 1050A: Use this alloy when you need the best thermal conductivity. It moves heat faster than other alloys, making it great for high-power devices.
- 6000-series alloys: These alloys balance thermal efficiency and easy manufacturing. They fit many uses, from computers to LED lights.
You also want to know how each alloy performs:
- 6061-T6: Thermal conductivity of 167 W/mK.
- 6063-T5: Thermal conductivity of 209 W/mK.
- 1050A: Superior thermal performance with 229 W/mK.
Most LED applications benefit from well-designed aluminum heat sinks. About 90% of these products use aluminum because it cools well and costs less than copper.
Note: You should always match the alloy to your needs. Think about strength, shape, and how much heat you need to move. The right choice helps your device last longer and work better.
If you want a heat sink that looks good, works well, and fits your budget, start with 6061 or 6063. For special needs, consider 1050A or other 6000-series alloys. You get the best results when you match the alloy to your project.
Choosing an Anodized Aluminum Heat Sink
Assessing Thermal Needs
You must start by understanding how much heat your device produces. This step helps you pick the right heat sink for your project. If you choose a heat sink that cannot handle the heat, your device may overheat or fail. You want to match the heat sink’s cooling power to your device’s needs.
Here are the main factors you should consider:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Performance and Conductivity | Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity moves heat away from components quickly. Lower thermal resistance means better cooling. |
| Size and Shape Constraints | The heat sink must fit your device and provide enough cooling. The shape affects how well it works. |
| Airflow and Cooling Method | Good airflow helps remove heat. You may use passive or active cooling, depending on your setup. |
| Material Quality and Durability | Anodized aluminum resists corrosion and works well in tough places. |
| Cost and Availability | Aluminum heat sinks offer a good balance between price and performance. |
You also want to look at how anodization improves performance. The anodized layer creates a porous surface. This layer increases the surface area and helps the heat sink give off more heat. Your device stays cooler and works better.
Tip: Always check the amount of heat your device makes. Pick a heat sink that can handle more than your highest heat level.
Size and Shape
The size and shape of your heat sink matter a lot. A bigger heat sink can move more heat away from your device. The shape, such as fins or blocks, changes how well the heat sink works.
- Anodizing makes the surface harder and helps it last longer.
- The process also boosts how well the heat sink gives off heat.
- You can pick different shapes and colors to fit your design.
Here is a table that shows how different shapes improve heat dissipation:
| Heat Sink Type | Average Heat Dissipation Improvement |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Foam | 17% |
| Finned Heat Sink | 31% |
| Aluminum Block | 44% |
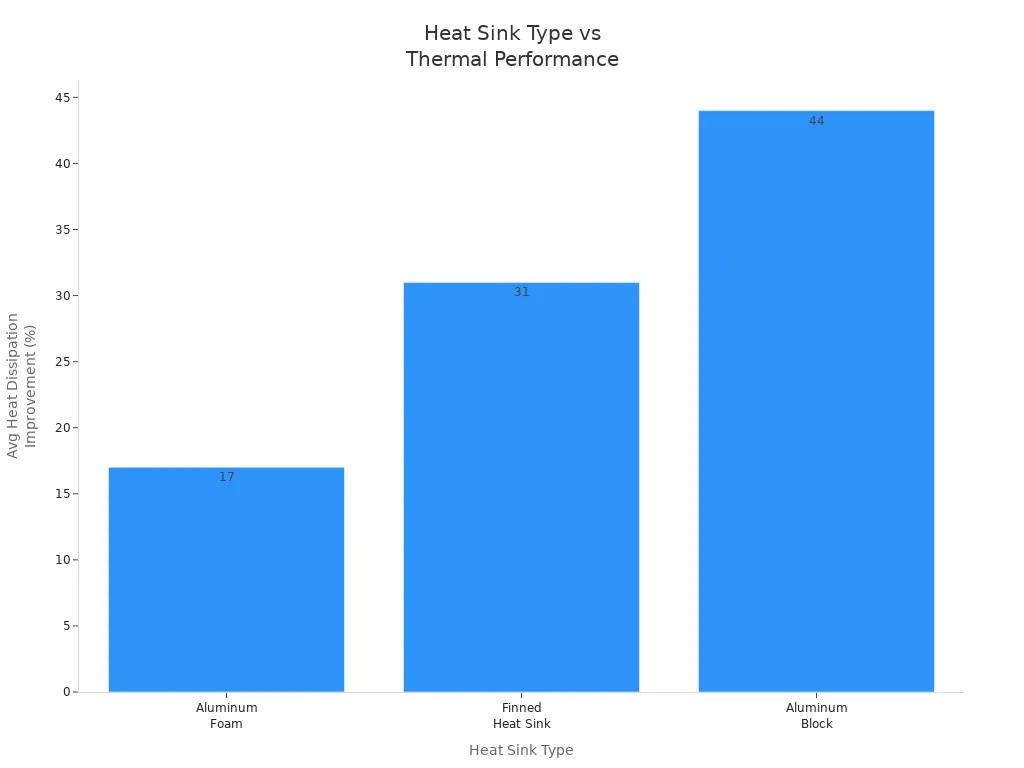
The study shows that finned heat sinks work better than foam types. Aluminum blocks give the highest improvement. You should pick the size and shape that fits your device and gives the best cooling.
Note: A larger surface area helps your heat sink cool better. Choose a shape that lets air move easily around the heat sink.
Airflow Considerations
Airflow plays a key role in how well your heat sink works. You want air to move across the fins or surface of the heat sink. This movement takes heat away and keeps your device cool.
- Airflow removes heat from the surface and stops heat from building up.
- You should make sure nothing blocks the air moving around the heat sink.
- Place the heat sink so air flows across the fins, not against them.
- Keep enough space around the heat sink for air to move freely.
- Use ducts or shrouds if you need to guide air in a certain direction.
Tip: Good airflow means better cooling. Always check that air can move easily around your anodized aluminum heat sink.
If you follow these steps, you will pick a heat sink that keeps your device safe and cool.
Surface Area Importance
You need to pay close attention to the surface area when you choose an anodized aluminum heat sink. The surface area controls how much heat your heat sink can move away from your device. A larger surface area lets more heat escape into the air. This keeps your electronics safe and working well.
You can increase the surface area by using special designs. Fins and pin fin shapes add more space for heat to leave the heat sink. These designs help air move around the heat sink and carry heat away faster. You get better cooling when you use these shapes.
- Finned heat sinks give you more surface area.
- Pin fin designs let air flow in many directions.
- More surface area means better cooling for your device.
The way your heat sink moves heat depends on two main methods: convection and radiation. Convection happens when air moves heat away from the surface. Radiation sends heat out as energy. Anodized aluminum helps with both methods because the anodized layer has high emissivity.
Here is a table that shows how each method helps with heat dissipation:
| Heat Transfer Method | Contribution to Heat Dissipation |
|---|---|
| Convection | About 30% or more in natural convection at sea level |
| Radiation | Big increase due to anodizing’s high emissivity |
You want to maximize the surface area to get the best cooling. This is true for both passive and active cooling systems. When you do this, you keep your electronics at safe temperatures and prevent overheating.
Tip: Pick a heat sink with more fins or a pin fin design if you need better cooling. More surface area means your device stays cooler.
Mounting and Contact Surface
You must make sure your heat sink has a clean and flat mounting surface. The way your heat sink touches your electronic part changes how well it moves heat. If the surface is rough or has gaps, heat cannot move easily. This makes your device get hotter.
A smooth and flat contact surface lowers the thermal resistance. This means heat moves from your device to the heat sink faster. You should check for any bumps or defects before you mount the heat sink. Use thermal paste or pads to fill tiny gaps and improve contact.
The pressure between the heat sink and your device also matters. You want even pressure so the whole surface touches. This helps heat move better and keeps your device cool.
Note: Always clean the mounting surface before you attach the heat sink. A good contact surface gives you the best cooling.
Cost and Application Fit
You need to think about cost when you pick an anodized aluminum heat sink. The price can change based on how many you order, the type of anodizing, and the shape of the part. If you order more heat sinks, the cost for each one goes down. Special anodizing types, like hardcoat, may cost more but give you extra protection.
Complex shapes or large heat sinks need more work to make. This can raise the price. If you want custom colors or extra cleaning, these services add to the total cost.
Here is a table to help you see what affects the cost:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Volume of Parts | Higher volumes lower the cost for each heat sink. Small orders cost more per piece. |
| Type of Anodizing Required | Some anodizing types cost more, especially for tough environments. |
| Part Complexity and Size | Complex or large heat sinks need more work and cost more. |
| Additional Services and Customization | Cleaning, masking, or special colors add to the total price. |
You should match the heat sink to your project needs and budget. Think about how much cooling you need, how many heat sinks you want, and what features matter most for your application.
Tip: Plan your order size and design to get the best value. Choose the right anodizing and shape for your needs.
Anodized vs Non-Anodized Heat Sinks
Performance Comparison
You want your heat sink to move heat away fast. The surface of the heat sink is very important. Anodized heat sinks have a special layer that helps them release heat better. Non-anodized heat sinks do not work as well. Look at the table below to see the difference:
| Type of Aluminum Heat Sink | Emissivity Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Anodized | 0.83 to 0.86 |
| Non-Anodized | 0.04 to 0.06 |
A higher emissivity means the heat sink lets out more heat. Anodized surfaces help your device stay cooler. This is extra helpful when you use passive cooling. Non-anodized heat sinks reflect most heat, so they do not cool well. If you want the best cooling, pick an anodized aluminum heat sink.
Tip: Anodized surfaces help with heat radiation. This keeps electronics safe.
Durability and Maintenance
You need a heat sink that lasts a long time. Anodizing gives aluminum a thick, hard layer for protection. Here are some ways anodized heat sinks are better:
- Anodizing makes a strong layer that stops corrosion.
- The protective coat is part of the metal, so it does not peel.
- Anodized heat sinks do not scratch or dent easily.
- The surface stays strong, even with lots of use.
- Anodized aluminum does not rust or get pits over time.
- The heat sink keeps working well, while untreated aluminum can get worse.
You will spend less time cleaning an anodized heat sink. The surface is smooth and easy to wipe. Non-anodized heat sinks need more care because they can rust or get damaged faster.
Note: Anodized heat sinks look good and work well for years, even in tough places.
When Anodizing Is Needed
You should pick anodizing if your heat sink faces water, chemicals, or rough use. Anodized heat sinks work best when you need extra protection and long life. Here are some times when anodizing is a good idea:
- Outdoor electronics or devices in wet places
- Machines that face dust, oil, or chemicals
- Devices that need to run for many years with little care
- Projects where you want a colored or special finish
If you want a heat sink that looks nice and works well for a long time, pick anodizing. You get better cooling, more protection, and less work over time.
Tip: Pick anodizing for projects where you need strong, safe, and cool heat sinks.
Common Questions and Misconceptions
Does Color Affect Performance?
You might think the color of your anodized aluminum heat sink changes how well it cools. Many people believe black anodized heat sinks work better than clear or colored ones. The truth is, color does not really change how much heat the heat sink can move. The most important thing is the anodized surface. This surface helps the heat sink give off heat and cool down by radiation and convection.
Here is a table that shows what matters most:
| Aspect | Effect on Thermal Performance |
|---|---|
| Anodized Surface Area | Helps heat leave the heat sink faster |
| Thermal Conductivity | Anodized coatings lower how fast heat moves |
| Oxide Layer | Makes heat sink release heat better |
| Thickness of Anodized Layer | Thin layers do not change cooling much |
Any anodized finish, like black, clear, blue, or green, works well. The finish and oxide layer help the heat sink get rid of heat. Color mostly changes how the heat sink looks or matches your brand, not how it cools.
Tip: Pick any color you like for style or to tell devices apart. You do not need to worry about losing cooling power.
Is Anodizing Always Required?
You may wonder if anodizing is needed for every aluminum heat sink. The answer depends on where you use it. Anodizing gives extra protection against rust and scratches. It also helps the heat sink send out heat better because it raises emissivity.
Here is a table that clears up some wrong ideas:
| Misconception | Reality |
|---|---|
| Anodizing makes aluminum weaker | Anodizing does not change how strong the metal is |
| Bare aluminum cools just as well | Anodizing helps heat leave the heat sink faster |
| Only black anodizing works best | All anodized colors cool about the same |
You should use anodized heat sinks in places with water, chemicals, or lots of use. If your device is in a clean, dry spot, bare aluminum might work. But you will not get the same protection or cooling.
Note: You do not always need anodizing, but it helps your heat sink last longer and work better.
Cleaning and Maintenance
You want your anodized aluminum heat sink to last and work well. Cleaning it the right way helps keep it in good shape. Follow these easy steps:
- Rinse gently with clean water to wash off dust.
- Mix a little pH-neutral dish soap in warm water.
- Use a soft cloth or sponge to wipe the surface.
- For tough dirt, use a soft nylon pad. Try it on a small spot first.
- Rinse again to remove all soap and dirt.
- Dry with a soft, clean cloth to stop water spots.
Tip: Do not use strong chemicals or scrub hard. This can hurt the anodized layer and make it work worse.
Clean your heat sink often to keep it looking new and working well. You do not need special tools or cleaners. Simple care helps your anodized aluminum heat sink last for many years.
When you pick an anodized aluminum heat sink, you get many good things. Corrosion resistance keeps your device safe from water and chemicals. The hard oxide layer stops scratches and damage. Electrical isolation helps stop short circuits. Enhanced emissivity helps the heat sink cool without fans. You can choose colors to match your brand.
You need to pick heat sink features that fit your project. Custom designs and smart choices make your device work better and last longer. For the best results, use ready-made molds or get a heat sink made just for you.
FAQ
How do you install an anodized aluminum heat sink?
First, line up the heat sink with your device. Use screws or clips to hold it in place. Put thermal paste between the heat sink and your device. Make sure the surface is clean and flat before you start.
Can you use anodized heat sinks outdoors?
Yes, you can use anodized heat sinks outside. The anodized layer keeps out rain and chemicals. It helps the heat sink last longer and stops rust.
Does anodizing affect electrical conductivity?
Anodizing makes a layer that does not let electricity pass. This layer keeps your device safe. It helps stop short circuits and makes things safer.
What colors are available for anodized heat sinks?
You can pick black, clear, blue, green, or other colors. The color does not change how well it cools. You can match your device or brand easily.
How do you clean an anodized aluminum heat sink?
Rinse the heat sink with water and use mild soap. Wipe it with a soft cloth. Do not use strong chemicals or rough pads. The anodized surface is easy to clean and does not stain.
Are anodized heat sinks safe for high-power electronics?
Yes, you can use them for high-power electronics. The anodized layer helps move heat away and protects the heat sink. Your device stays cool and safe.
Can you customize the shape of an anodized heat sink?
You can make different shapes when you create the heat sink. Fins, pins, and blocks are popular choices. Custom shapes help cool your device and make it fit better.
How long does the anodized finish last?
The anodized finish lasts for many years. It does not fade, scratch, or rust easily. You get a heat sink that works well and looks good for a long time.




