What Are Liquid Cooling Plates and How Do They Function in Modern Systems
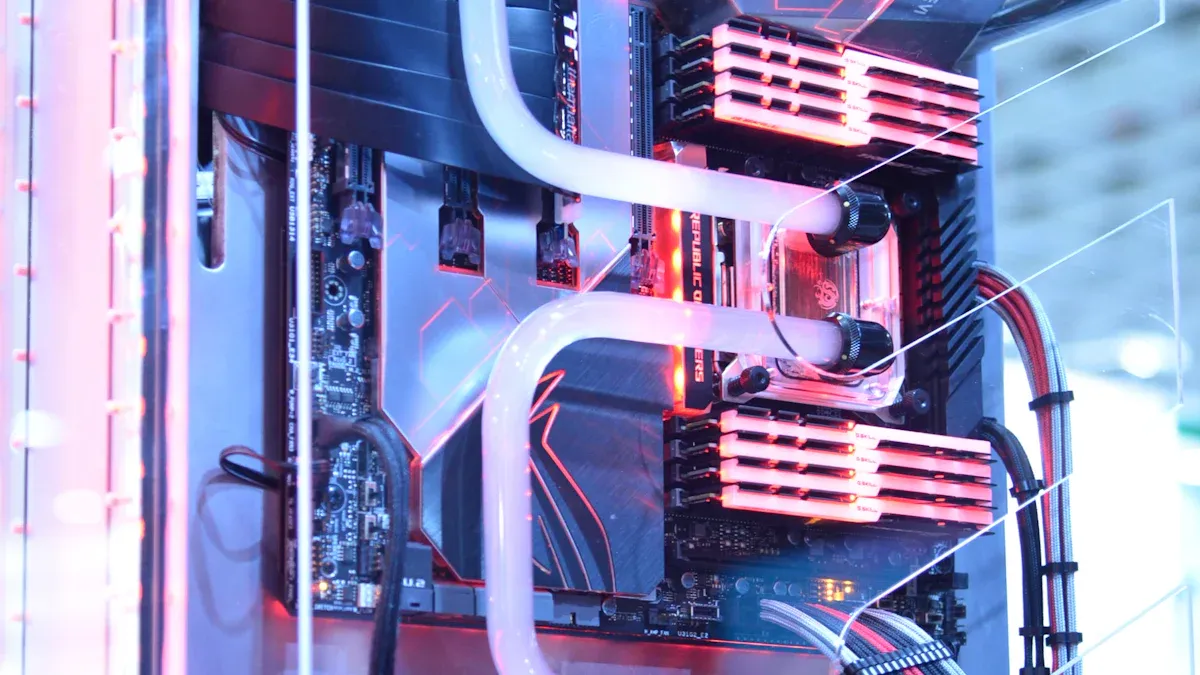

Liquid cooling plates help manage heat in modern systems. These plates move liquid over a surface. The liquid takes heat away from important parts. Liquid cooling plates cool better than forced air cooling.
| Cooling Method | Effectiveness in Heat Transfer |
|---|---|
| Liquid Cooling | Up to 4 times more effective |
| Forced Air Cooling | Less effective |
- You get steady and strong cooling.
- Your system can last longer.
- You lower the chance of overheating.
Liquid cooling plates help high-performance equipment work well. You can trust your devices to work hard without problems.
Key Takeaways
- Liquid cooling plates work better than air cooling. They can remove heat up to four times more. This helps your system stay cool and work well.
- Liquid cooling helps your devices last longer. It stops them from getting too hot. This means you will need fewer repairs and replacements.
- Pick the best materials for your cold plates. Copper moves heat the best. Aluminum is lighter and costs less for easier jobs.
- You must take care of your cooling system. Clean it often and check the coolant levels. This helps it work its best.
- Liquid cooling plates can be used in many ways. They work in computers, electric vehicles, and other industries. They can fit many different cooling needs.
Liquid Cooling Plates Overview

Definition
Liquid cooling plates help move heat away from important parts. People also call them cold plates. They work as heat exchangers. The plates have metal surfaces with channels or fins inside. When liquid moves through the channels, it takes heat from the device. The liquid then carries the heat away.
In the IT industry, a ‘cold plate’ is a heat exchanger. It is usually made of metal with fins and channels. It moves heat from powerful processors to a cooling liquid. The liquid is pumped through the channels to take in heat. Cold plates are like terminal units in a chilled water system. They have special needs for temperature, flow, pressure drop, material, and cleanliness.
Liquid cooling plates are used when air cooling is not enough. They are found in computers, electric vehicles, and other strong systems. They help control heat better and keep equipment safe from getting too hot.
Core Function
Liquid cooling plates use a closed-loop system to keep things cool. Each part works together, as shown in the table below:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cold Plates | Give direct cooling to CPUs or GPUs for best results. |
| Heat Rejection Units (HRUs) | Cool the vapor back into liquid, using air or water designs. |
| Manifold | Moves fluid from the HRU to the cold plates and sends vapor back, with two chambers inside. |
| Software Defined Cooling (SDC) | Watches HRU performance, checks for leaks, and works with other software. |
A pump starts the process by moving liquid through the cold plate. The liquid flows in the channels and picks up heat. Then, it goes to the heat rejection unit. The heat rejection unit cools the liquid down. The liquid returns to the cold plate. This cycle keeps repeating, so the system stays cool.
Liquid cooling plates can handle more heat than old cooling ways. You can see the difference in the table below:
| Cooling Method | Heat Dissipation Capacity | Efficiency in High-Performance Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Cold Plates | Better at removing heat from strong parts | Great for high-performance devices |
| Traditional Methods | Not as good, struggles with lots of heat | Not good for small, powerful designs |
You get steady cooling even when your device works hard. This helps your system run well and last longer.
Structure and Manufacturing
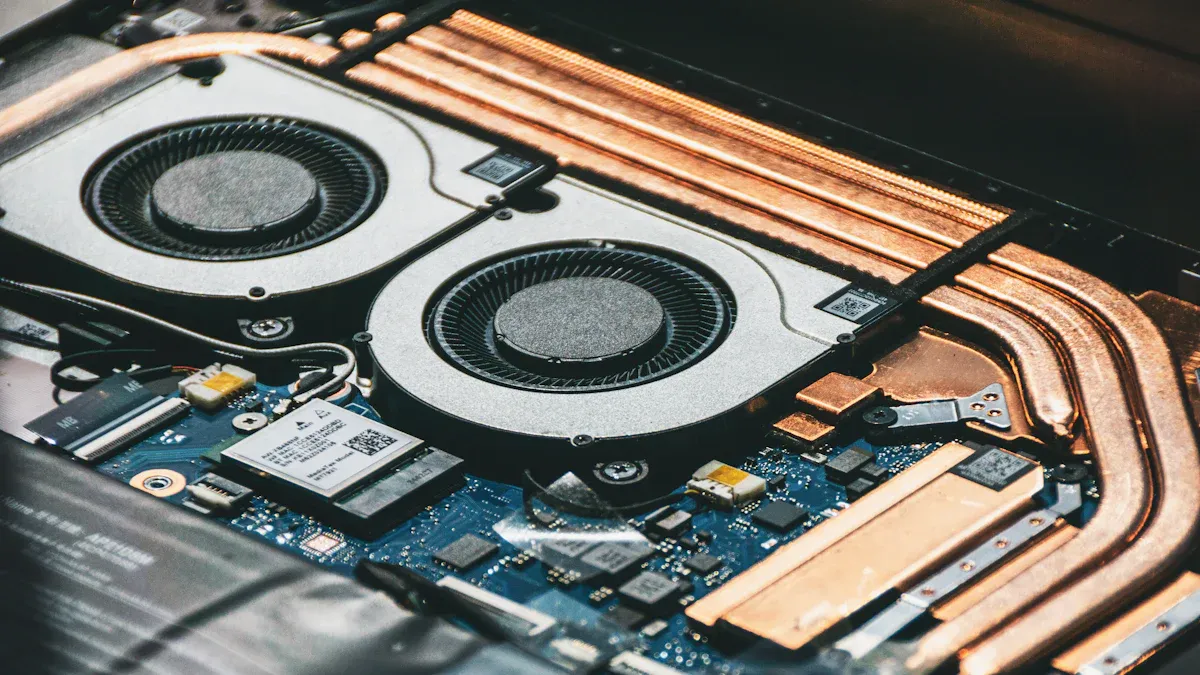
Materials
It is important to know what makes a good cold plate. Most cold plates use copper, aluminum, or composites. Each material helps move heat away in its own way.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 150-250 |
| Copper | >380 |
| Composites | 50-200 |
Copper moves heat the best. It has the highest thermal conductivity. You often see copper in cold plates for strong systems. Aluminum is lighter and costs less money. It works well for most devices that do not need top cooling. Composites are a mix and balance weight and performance.
When picking a material, think about more than heat transfer. Here is how copper and aluminum are different:
- Copper costs more and uses more energy to make.
- Aluminum is cheaper and easier to shape.
- Copper is heavy, so shipping and setup can be harder. Aluminum is light and easy to handle.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity | Weight | Cost | Durability | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High | Heavy | Higher | Superior | Excellent |
| Aluminum | Moderate | Light | Lower | Good | Susceptible |
Copper is best for high-performance systems. Aluminum works for low or medium-performance systems. If you want your cold plate to last long, copper is more durable and resists rust better.
Designs
The design of a cold plate changes how well it cools. There are several main types:
- Micro-channel cold plates have tiny channels. These help the liquid touch more area. This means better heat transfer and less resistance.
- Stamped cold plates use stamping to make them stronger.
- Roll bond cold plates use bonding to help with heat transfer.
- Extruded cold plates have channels made by pushing metal through a die. You can get flat or twisty tubes. These designs change how fast the liquid moves and how even the temperature stays.
- Machining plus friction stir welding (FSW) cold plates use cutting and welding. This makes strong and high-performing plates.
The way channels are designed inside the plate matters. It changes how fast the liquid moves and how well heat spreads. Some designs make the plate stronger, so your system lasts longer.
Processes
There are different ways to make a cold plate. Each way has good and bad points.
| Manufacturing Process | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Extrusion | Fast, cheap, many shapes and sizes | Only for simple shapes, not for complex designs |
| Machining | Flexible, smooth surface | Expensive, slow, wastes material |
| Bonding | Accurate size, smooth finish | Expensive, takes more time |
| Additive Manufacturing | Flexible, makes complex shapes, quick | May be weaker, size limits |
Advanced techniques make cold plates even better. Friction stir welding (FSW) gives seamless joints. This helps heat move better. Vacuum brazing makes strong, leak-proof joints. This is good for high-pressure systems. Tube embedding lets you fit cooling into small spaces.
| Technique | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Friction Stir Welding (FSW) | Seamless bonding, better heat transfer |
| Vacuum Brazing | Strong, leak-proof joints, good for high pressure |
| Tube Embedding | Compact and efficient thermal management |
Using liquid cooling plates helps your system stay cool and work well. The right material, design, and process matter a lot. You also need to plan how the cold plate fits with other parts. Good planning helps your electronics work better and last longer.
Advantages
Efficiency
Liquid cooling plates cool things better than air cooling. They move heat away from devices very fast.
- Liquid cooling systems use less power than air cooling. Their Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) can be under 1.1. Air-cooled systems have a PUE of about 1.60.
- Faster liquid flow keeps chips at steady temperatures.
- You can remove more heat but use less energy.
- This helps you save money and makes your data center greener.
Tip: Using cold plates can lower energy use and cut greenhouse gases by up to 16%. If you add renewable energy, you can save up to 50% water.
Reliability
Cold plates help devices last longer. They keep electronics cool and slow down damage.
- Tests show cold plate assemblies work well with heat, moisture, and stress.
- A smooth cold plate surface helps thermal interface materials (TIMs) last 30–50% longer.
- Cooler temperatures protect batteries and chips. For example, a lithium-ion battery loses 70% of its power after 500 cycles at 55°C. If the temperature goes up by 13°C, the battery life is cut in half.
Note: Cold plates help your system work well even in hard conditions.
Flexibility
You can use cold plates in many places. Their design fits different needs and jobs.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom Flow Paths | You can make flow paths for special cooling needs. |
| Configurations | You can set up cold plates for different heat problems. |
| Industry Adaptability | Cold plates work in computers, cars, and machines. |
- Cold plates take away extra heat from semiconductors and microprocessors.
- They help cool tight spaces where air cooling does not work.
- Cold plates keep up with higher power needs in new devices.
Applications of Liquid Cooling Plates
Computers
Cold plates are used in powerful computers. These computers need strong cooling for CPUs and GPUs. Cold plates connect right to the processors. Water moves through small channels inside the plate. This setup works better than regular heat sinks. It helps move heat away faster.
Some data centers use immersion cooling. Electronics sit in a special liquid. This cools them without fans or compressors. It works well for server racks that are packed close together.
Here is a table that explains how cold plates help computers:
| Application Type | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU Cold Plates | Cold plates with small channels and moving water cool CPUs and GPUs. |
| Immersion Cooling | Electronics are put in liquid for better cooling. |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency | Liquid cooling moves heat away from the source, so warmer liquids can be used and cooling is better. |
Tip: Cold plates let you use powerful computers without getting too hot. You get steady speed and your hardware lasts longer.
Electric Vehicles
Cold plates keep electric vehicle batteries cool. The plates touch the battery cells and pull heat away fast. The cooling system uses pumps and heat exchangers to move the liquid.
Cold plates must fit many battery shapes and sizes. Good design gives even cooling and keeps batteries safe.
If batteries are not cooled well, they may not work right or could be unsafe. Cold plates move heat from the battery to the coolant. The coolant then lets go of the heat through a heat exchanger.
Cold plates are also used in electric vehicle powertrains. They keep inverters and other parts at the right temperature. A two-pass design spreads cooling so no part gets too hot.
Cold plates help save energy and make batteries last longer.
- Cold plates touch battery cells for better heat transfer.
- The cooling system has pumps and heat exchangers.
- Even cooling keeps batteries working well and safe.
- Good temperature control helps save energy.
Industry
Cold plates are used in many industries. They cool renewable energy systems, medical tools, lasers, and power supplies.
Data centers use cold plates to cool servers. New designs use hybrid cooling and special fluids to help the environment.
Cold plates are also found in defense, avionics, and telecom equipment.
Stamped cold plates cost less and are good for making many at once. Aluminum is used a lot because it is easy to shape and costs less than copper.
You can find cold plates in electric car chargers, UPS units, and telecom rectifiers.
- Cold plates cool IGBTs, lasers, and batteries.
- Data centers use different cooling types for AI work.
- Medical and defense tools need cold plates to stay cool.
- Stamped plates help save money when making lots of them.
Note: Cold plates help meet tough cooling needs in many jobs. You get better results and spend less money.
Practical Considerations
Maintenance
You must keep your cold plate system clean and working. Regular care helps it last longer and work better.
- Flush and refill the system with the right coolant mix.
- Check the pH of the coolant often. If it is below 4.0 or above 9.0, flush and refill.
- Measure the fluid’s pH and refractive index to know when to clean.
- Make flow lines smooth and lower turbulence to stop erosion and corrosion.
Tip: Always use clean copper alloys or stainless steel. Do not use carbon steel because it can rust. Make sure all parts are clean before building. Blow out water and use nitrogen gas to dry the system before shipping. Keep the cooling loop clean during installation. Use brazing instead of soldering. Keep checking pH, water conductivity, bacteria, and corrosion inhibitors.
Condensation
Condensation can cause trouble for cold plates. If the plate is colder than the air, water drops may form. These drops can hurt electronics.
You can stop condensation by:
- Keeping the coolant temperature above the dew point.
- Putting insulation around cold plates and pipes.
- Watching the humidity in the room.
Note: If you see water drops near your cold plate, check the temperature and add insulation.
Misconceptions
Some people think wrong things about liquid cooling plates.
- Immersion cooling and direct-to-chip cooling are not the same.
- Not all systems use water as coolant. Some use special fluids.
- A water leak can cause big damage and stop work. It is not safe.
When you pick a cold plate, look at these things:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Performance | Pick a cold plate that can handle your heat load. |
| Manufacturing Cost | Choose a type that fits your budget and cooling needs. |
| Size and Weight | Lightweight plates work best for aerospace and tight spaces. |
| Installation and Maintenance | Simple designs are easier to install and care for. |
| Fluid Compatibility | Make sure the coolant matches the plate material. |
| Operational Environment | Think about temperature, humidity, and corrosion risks. |
| Scalability and Future-Proofing | Pick designs that allow upgrades and work with your current system. |
If you put a cold plate in an old system, watch for debris, corrosion, and bacteria. These can clog the plate and cause problems. You need to connect fluid lines and electrical ones, which makes it harder to install. Always use good coolant to stop deposits and corrosion.
You now know that liquid cooling plates help keep systems cool. These plates use liquid to take heat away from key parts. This helps your system work better and stay safe. You get better cooling, more power in small spaces, less energy use, and less noise.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved thermal performance | Liquids move heat better than air. This helps remove heat from strong parts. |
| Greater compute density | Good cooling lets you put servers close together. They do not get too hot. |
| Lower energy use and environmental impact | Liquid cooling means you use less air conditioning. This saves energy and helps the planet. |
| Reduced noise and maintenance requirements | Liquid cooling makes less noise. It has fewer moving parts, so it is quieter. |
You should use liquid cooling plates if your system needs better cooling. They are good for high-power devices. If you have special needs, you can get a custom cold plate for your system.
FAQ
What is the main job of a cold plate?
A cold plate moves heat away from important parts in your device. You use it to keep things cool when air cooling does not work well. Cold plates help your system stay safe and last longer.
Can you use a cold plate with any liquid?
You should use the right coolant for your cold plate. Water works for many systems, but special fluids can help stop rust or freezing. Always check if the coolant matches the cold plate material.
How do you know if your cold plate needs cleaning?
You may see less cooling or higher temperatures. If your cold plate has dirt or buildup inside, it cannot move heat well. Check your system often and clean the cold plate when you see these signs.
Will a cold plate make my computer quieter?
Yes, a cold plate can lower noise. It uses liquid to move heat, so you do not need as many fans. Your computer can run cooler and quieter with a cold plate.
Is a cold plate safe for home use?
A cold plate is safe if you install it right and check for leaks. Use the correct coolant and follow the maker’s instructions. You can use a cold plate at home for computers or other devices.




