The Function and Benefits of Copper Heat Pipe Heat Sinks
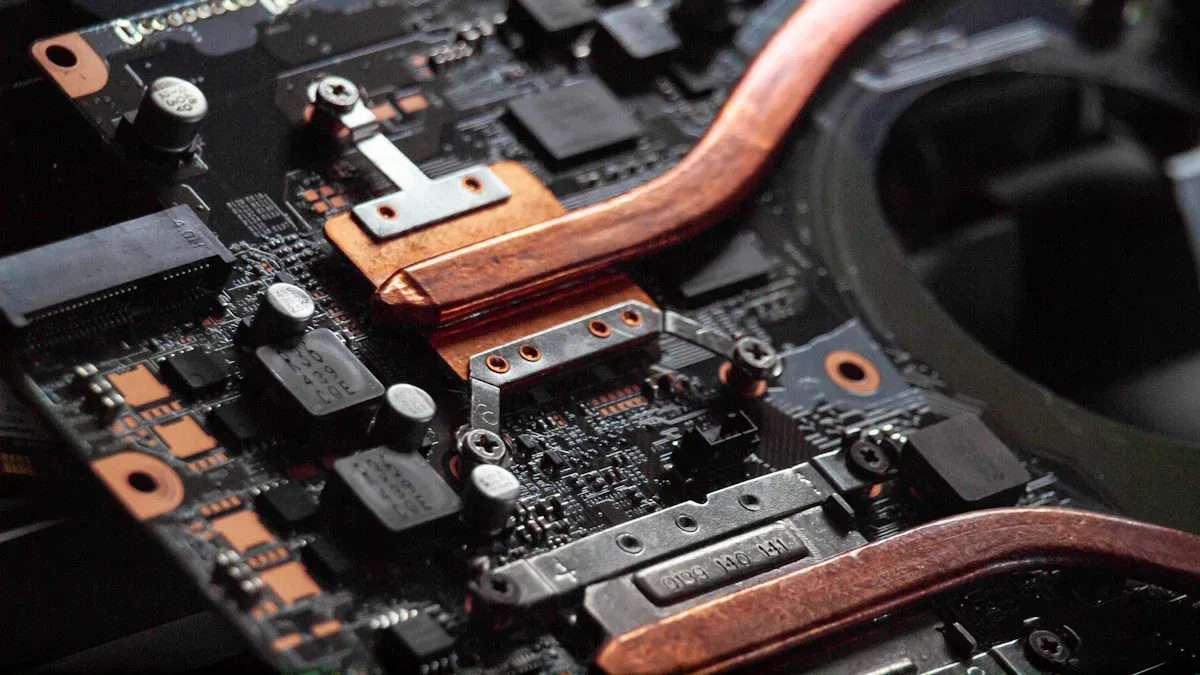
You use copper heat pipe heat sinks to cool your devices. These help your devices work well and not overheat. More than half of electronic problems happen because heat is not removed well. Cooling solutions are very important for good performance and reliability. Copper is special because it moves heat much better than aluminum. Its thermal conductivity is almost twice as high. A custom heat pipe heat sink from a trusted heatsink manufactory can move heat away quickly. This protects your electronics and helps them last longer. With a custom heat sink, you get better efficiency and feel more confident.
Key Takeaways
- Copper heat pipe heat sinks take heat away fast. They help devices stay cool and work well. The design uses water vapor and a wick. This moves heat faster than just metal. These heat sinks last a long time, over 15 years. They work well in any position. Using copper heat pipe heat sinks saves energy. They lower the need for fans. This helps devices run smoothly. They work in many places, like computers and factories. They are also used in satellites. They help devices stay safe and work better.
Copper Heat Pipe Basics
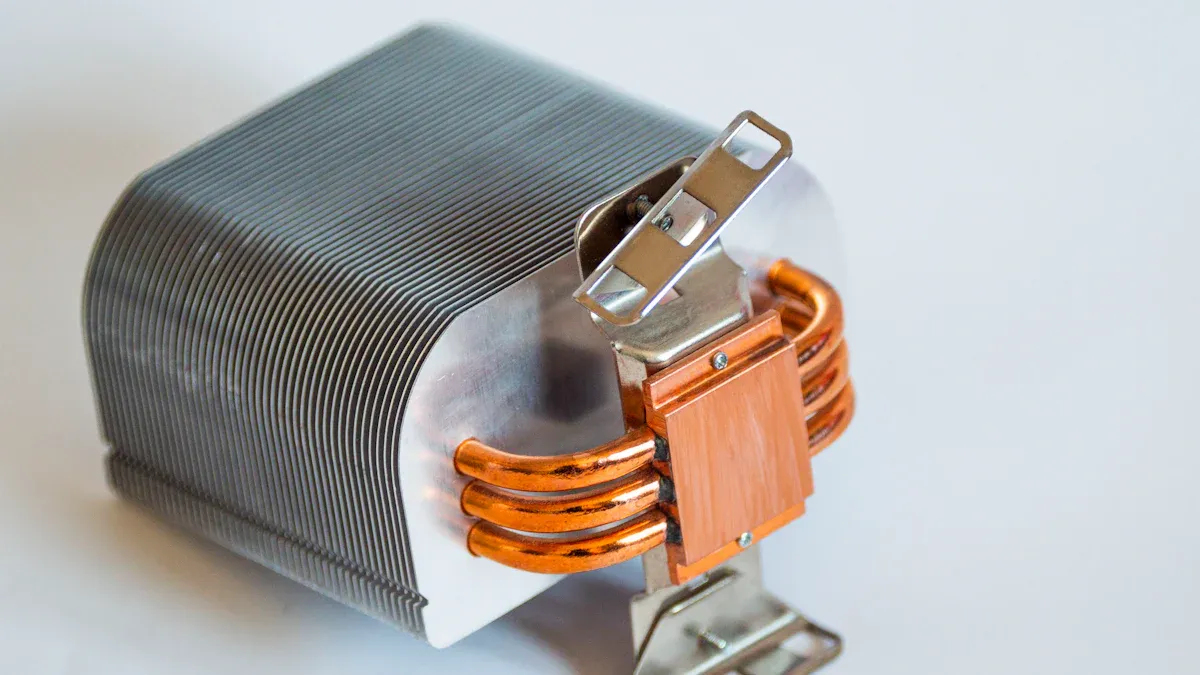
Structure
You find three main parts inside a copper heat pipe. Each part plays a special role in moving heat away from your device. The table below shows these parts and how they help with heat transfer:
| Component | Description | Contribution to Heat Transfer Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Enclosure | Vacuum-sealed tube, usually made of copper. Thin walls, sometimes as little as 0.4 mm thick. | Copper gives a strong, thermally conductive path. The vacuum stops air from slowing down heat movement. |
| Wick Structure | Lines the inside wall. Can be sintered powder, mesh, or grooves. | The wick pulls liquid back to the hot end using capillary action. This keeps the cycle going and spreads heat evenly. |
| Working Fluid | Water fills the inside. It changes from liquid to vapor and back. | The phase change lets the pipe move heat much faster than solid metal alone. |
You see copper used for both the enclosure and the wick. Copper works well because it has high thermal conductivity and resists corrosion. The enclosure gets vacuum-sealed after adding water, which helps the copper heat pipe last for many years.
Working Principle
A copper heat pipe works by moving heat from one end to the other very quickly. When your device heats up, the hot end (called the evaporator) absorbs this heat. The water inside turns into vapor. This vapor travels to the cooler end (the condenser), where it gives up its heat and turns back into liquid. The wick then pulls the liquid back to the hot end, and the cycle repeats.
The wick structure is important. It uses tiny pores to create capillary action, which means it can move liquid even against gravity. Some wicks combine different materials and shapes to balance strong capillary force with easy liquid flow. This design helps the copper heat pipe handle more heat and work in any position.
Water is the best working fluid for most copper heat pipes. It matches well with copper and works best at temperatures between 100°C and 150°C. You get reliable performance and long life because water and copper do not react badly with each other.
Copper heat pipes can move hundreds of watts of heat, even in small sizes. They keep your electronics cool and safe, even when working hard.
Benefits
Thermal Conductivity
Copper heat pipe heat sinks move heat very well. The liquid inside changes to vapor and back again. This helps heat travel faster than in solid copper. Solid copper has a thermal conductivity of about 390 W/m-K. Copper heat pipe heat sinks can reach from 1,500 up to 50,000 W/m-K. This big increase happens because the vapor carries heat quickly to the cool end. The vapor turns back to liquid and gives off heat. This makes the process work really well. Smaller pipes can move heat even better. This helps cool powerful devices and keeps their temperature steady.
A study showed aluminum heat sinks with copper heat pipes work almost as well as solid copper heat sinks. The temperature difference was only about 9.2°C for one part. This shows copper heat pipe heat sinks cool well without being heavy or costly.
Fast Response
Copper heat pipe heat sinks react fast to temperature changes. The phase change inside lets heat move quickly from hot spots to cool areas. You get lower thermal resistance and better heat spreading than with regular copper heat sinks. Vapor chambers and heat pipes can reach over 5,000 W/m-K. Solid copper stays around 401 W/m-K. This quick response stops your device from overheating when power use jumps.
Tip: Fast heat transfer helps your device handle short bursts of high power. This keeps it from getting too hot and protects important parts.
Reliability
Copper heat pipe heat sinks last a long time. Tests show they can work for about 147,456 hours, or almost 17 years, at 60°C. Some big copper heat pipes have worked for over 20 years in hard places like trains and wind turbines. Makers test them to find early problems, so you get a product that works well for many years.
Copper heat pipe heat sinks also stop hot spots in electronics. Copper wick structures, like metal foam, help move heat and liquid better. This keeps the temperature even and stops dry spots near hot areas. Tests show copper heat pipe heat sinks can lower hot spot temperatures by up to 7.7°C under heavy use. Thicker copper heat spreaders help spread heat more evenly. This protects your device and helps it last longer.
You also save energy with copper heat pipe heat sinks. Their good design and high thermal conductivity mean fans do not need to run at full speed. This uses less energy and keeps your device quieter. Stable temperatures stop your device from slowing down to protect itself. You get better performance and use less power.
- Copper heat pipe heat sinks move heat fast, even with small temperature changes.
- You use less energy because fans do not work as hard.
- Steady temperatures mean fewer slowdowns and less wasted energy.
- Long life means less fixing and fewer replacements.
Note: Hybrid cooling systems with copper heat pipes and phase change materials or metal foams can save even more energy and cool better.
Applications

Electronics
Copper heat pipe heat sinks are in many electronics. You find them in computers, laptops, and gaming consoles. These heat sinks help keep CPUs and GPUs cool. When you play games or use big programs, your device gets hot. Copper heat pipes move the heat away from the processor fast. This keeps your computer safe and working well. Designers pick copper heat pipes because they move heat better than other materials. This helps your electronics last longer and work better, even when you use them a lot.
Industrial
Factories and power plants use copper heat pipe heat sinks in big machines. These heat sinks move heat from hot spots to cooler places. This helps machines work smoothly and not overheat. You can find them in systems with silicon carbide (SiC) power devices. These devices get very hot, but copper heat pipes spread the heat out. Some heat sinks have special fins to let air flow better and remove more heat. Engineers can bend or flatten the heat pipes to fit small spaces. This makes copper heat pipe heat sinks a good choice for many factory jobs.
- Copper heat pipe heat sinks can:
- Lower thermal resistance by up to 50% compared to regular heat sinks.
- Make temperatures more even, so nothing gets too hot.
- Work well in high-power servers and SiC inverters.
Note: You get better cooling and use less energy, but you might need stronger fans for the best results.
Emerging Uses
New technology uses copper heat pipe heat sinks for better cooling. Satellites use these heat sinks to cool powerful chips. They move heat quickly, even in space, and keep things steady. Data centers and telecommunication systems use copper heat pipes to cool blade servers. These servers do many jobs at once and need strong cooling to keep from slowing down. The thin shape of copper heat pipes lets them fit in small spaces but still move a lot of heat. You also see these heat sinks in edge computing and other high-tech areas where devices must stay cool to work well.
You get cooler devices and they last longer with copper heat pipe heat sinks. These heat sinks move heat fast and do not make much noise. They keep your electronics safe and steady.
- You find them in computers, factories, and satellites.
- They spread heat out, stop hot spots, and help devices work longer.
- You also use less energy and your device is quieter.
Experts say copper heat pipe heat sinks are great for strong cooling. They work in any position and do not need much care.
If you want cooling that works well and lasts, try this for your next project.
FAQ
What makes copper heat pipe heat sinks better than regular heat sinks?
Copper heat pipe heat sinks move heat much faster than regular heat sinks. You get better cooling for your devices. The vapor inside spreads heat quickly, so your electronics stay safe and last longer.
How long do copper heat pipe heat sinks last?
You can expect copper heat pipe heat sinks to work for many years. Most last over 15 years with normal use. You do not need to replace them often.
Can you use copper heat pipe heat sinks in any position?
Yes, you can use copper heat pipe heat sinks in any position. The wick inside moves liquid back to the hot end, even if you turn the device sideways or upside down.
Are copper heat pipe heat sinks safe for all electronics?
You can use copper heat pipe heat sinks with most electronics. They work well with computers, servers, and even power devices. Always check your device’s needs before choosing a heat sink.
Do copper heat pipe heat sinks need much care?
You do not need to do much to take care of copper heat pipe heat sinks. They work without moving parts. Just keep them clean and make sure air can flow around them.




