How to Choose the Right Heat Sink for Your Application
You want your electronic devices to work for a long time. Heat sink selection is important because it helps keep your device cool. This helps your device work well. Choosing the right heat sink is crucial for safety and for your device to function properly. When you make a good heat sink selection, you help prevent your device from overheating and potentially failing.
- Good heat dissipation keeps the temperature safe.
- Getting too hot can damage electronic components.
- Using heat sinks effectively makes devices last longer and perform better.
When Is a Heat Sink Needed?

You should know when your device needs a heat sink. This helps keep your electronics safe and working well. If you do not check, your device might get too hot and break. There are some signs that show if you need a heat sink. The table below lists the most common signs:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Figure this out by using the highest power your device will use and the hottest temperature your part can handle. This stops overheating. |
| Power Dissipation | You need to find out how much heat your heat sink must remove. Use this formula: Power Dissipation = Pin – Pout. |
| Maximum Allowable Temperature | Learn the highest temperature each part can take. This helps you avoid damage and makes your device last longer. |
Power Dissipation Assessment
You have to check how much heat your device makes. This is called power dissipation. You can find it by measuring the power going in and the power coming out. The difference is the heat your device makes. You can use a tool called a Power Probe. It measures voltage and current at the same time. This helps you know how much power your device uses. You can also use a shunt resistor. This small part helps you measure current by checking the voltage drop across it. These ways help you find problems fast and keep your device from getting too hot. Knowing power dissipation helps you pick the right heat sink.
Allowable Temperature Rise
You need to know how hot your device can get before it gets hurt. Every part has a highest temperature it can handle. You should look at the datasheet to find this number. If your device gets close to this temperature, you need a heat sink. You want to keep the temperature rise under the limit. This helps your device last longer. By knowing both power dissipation and allowable temperature rise, you can decide if you need a heat sink for your device.
Thermal Resistance Calculation
Knowing about thermal resistance helps you pick the right heat sink. Thermal resistance shows how well a heat sink moves heat away. You want your device to stay cool and safe. So, you need to know how to figure out this value.
Junction and Ambient Temperatures
First, look at two main temperatures. The junction temperature is the hottest your part can get. The ambient temperature is the air around your device. The difference between these tells you how much heat must move away.
The formula for maximum thermal resistance is:
Maximum Thermal Resistance (K/W) = (Max Junction Temp – Ambient Temp) / Heat Output
If the air gets warmer, your device has to work harder. Higher air temperature means more heat to remove. You need a heat sink that keeps the junction temperature safe.
Power Dissipation Formula
You also need to know how much power turns into heat. This is called power dissipation. You can use easy formulas to find this number. The most common ones are:
| Power Dissipated (P) | Formula |
|---|---|
| Power Dissipated | P = V x I |
| P = V² / R |
- V means voltage.
- I means current.
- R means resistance.
After you know power dissipation, use it in the thermal resistance formula. This helps you pick the best heat sink. Picking the right heat sink keeps your device safe and working well.
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| Rth = ΔT/Q = (T_heat_sink – T_ambient) / P_loss | This formula finds thermal resistance. ΔT is the temperature difference. Q is the heat flow. T_heat_sink is the heat sink temperature. T_ambient is the air temperature. P_loss is the power loss. |
Tip: Always check your device’s datasheet for the highest junction temperature. Use real numbers for voltage and current.
Heat Sink Selection Process
Choosing the right heat sink for your device involves more than just picking a part from a catalog. You need to understand how heat moves through your system and how each part of the path affects cooling. This process helps you make smart decisions during heat sink selection.
Breaking Down the Thermal Path
You can think of the thermal path as the journey heat takes from your electronic component to the air around it. Each step in this path adds some resistance to heat flow. If you want your device to stay cool, you need to look at every part of this path.
- The surface temperature of your device depends on the internal thermal resistance.
- Heat moves from the chip to the case, then to the heat sink, and finally to the air.
- Heat travels by conduction (through solid parts), convection (through air or liquid), and radiation (through electromagnetic waves).
- The effectiveness of heat transfer to the air is very important.
Tip: Always check the datasheet for your component. Datasheets give you important numbers like thermal impedance and power dissipation. You can also find thermal curves that show how temperature changes with power. These tools help you make better choices during heat sink selection.
Simulation tools can also help you. They use computer models to show how heat will move in your design. This lets you test different heat sink options before you build anything.
Interface Materials
The materials between your device and the heat sink matter a lot. These are called thermal interface materials. They fill tiny gaps and help heat move from the chip to the heat sink.
When you choose a thermal paste or pad, follow these steps:
- Look at the material properties. Aluminum and copper heat sinks expand differently, so pick a thermal paste that matches.
- Think about the operating temperature and how much heat your device makes. Make sure the thermal paste can handle these conditions.
- Pick a thermal paste that stays good over time and does not break down at high temperatures.
- Check that the thermal paste works with any coatings or treatments on your heat sink.
Reviewing all thermal resistances, including those from interface materials, helps you understand how heat moves in your system. Even if some parts, like the backplate, do not change the hottest spot much, they help spread heat and keep your device safe.
Airflow and Mounting
How you mount your heat sink and how air moves around it can change how well it works. Good airflow helps carry heat away faster.
| Performance Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Surface Area | A larger area lets more heat escape. |
| Airflow | Clear, strong airflow cools your device better. |
| Thermal Resistance | Lower resistance means better heat transfer. |
You should place your heat sink where air can move freely. Avoid blocking the fins or putting the heat sink in a tight space. If you use a fan, make sure it blows air across the heat sink. This boosts cooling.
Environmental factors like dust and humidity can also affect cooling. Dust can block airflow and make the heat sink less effective. Humidity can change how heat moves through the air. Clean your device often and keep it in a safe place.
You also need to think about rules and standards. Some devices must meet safety or industry rules. These rules can set limits for temperature, size, or even the type of heat sink you can use.
| Requirement Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Specifications | Limits for temperature, power, and environment. |
| Physical Constraints | Size, weight, and space limits. |
| Regulatory Standards | Must follow safety and industry rules. |
Note: Always review all thermal resistances in your system. This includes the chip, interface materials, heat sink, and even the air around your device. Matching the thermal resistance of your heat sink to your application keeps your device safe and working well.
By following these steps, you can make smart choices during heat sink selection. You will keep your device cool, safe, and reliable.
Types of Heat Sinks
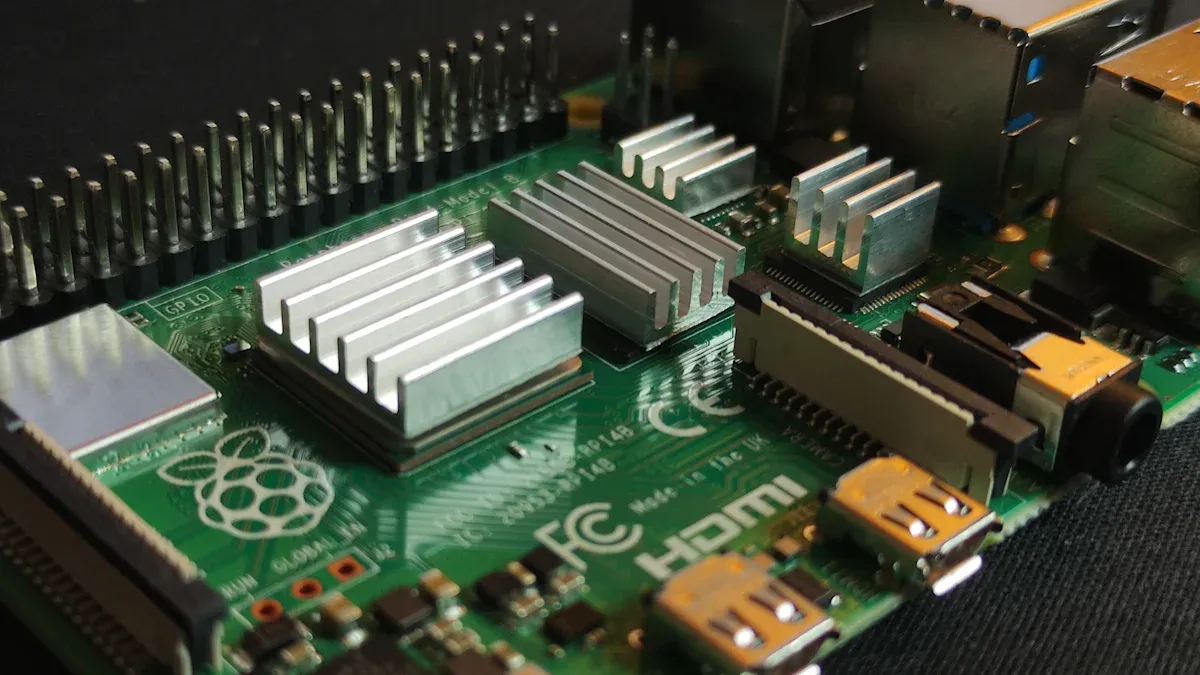
When you look at heat sink selection, you will find many types of heat sinks. Each type works best for different needs and environments. You should know the main categories before you choose.
Stamped, Extruded Skived, and Bonded Fins
You can pick from several common heat sink designs:
- Stamped fins use thin metal sheets pressed into shape. These work well for low-power devices.
- Extruded fins are made by pushing aluminum through a die. These offer strong cooling for medium to high-power electronics.
- Skived fins are sliced from a solid block, giving you high fin density and better cooling in tight spaces.
- Bonded fins attach extra fins to a base, which helps when you need more surface area for heat to escape.
You will also see other types in the market:
- Passive heat sinks stay quiet and simple.
- Active heat sinks use fans to move air and boost cooling.
- Hybrid systems combine both passive and active features.
- Liquid cooling systems use liquid to carry heat away.
- Heat pipe systems move heat quickly using phase change.
Liquid Cold Plates for High-Power Applications
If your device makes a lot of heat, you may need liquid cold plates. These use water or coolant to pull heat away fast. You often see them in power electronics like MOSFETs and thyristors. Liquid heat sinks work well when air cooling is not enough.
Vapor Chamber and 3D Technologies
Vapor chambers spread heat evenly across the heat sink. This helps stop hot spots. New 3D-printed heat sinks use less material and fit into small spaces. You can find these in data centers and advanced computers. Designers use thermal simulations to make sure these heat sinks work well and save energy.
Heat Pipe Integration for Enhanced Thermal Performance
Heat pipes move heat from one place to another using a special liquid inside. You get fast and even cooling. Many high-performance heat sinks use heat pipes to handle more power without getting too big.
Application Suitability
You need to match the heat sink type to your device. The table below shows what to check:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Geometric dimensions | Width, height, base thickness, and length of the heat sink. |
| Maximum thermal resistance | The highest thermal resistance your device can handle. |
| Maximum power loss | The most heat your device will make. |
| Orientation | The best way to place the heat sink for cooling. |
| Thermal paste | Use paste to fill gaps and help heat move. |
| Fastening | Make sure the heat sink stays tight on your device. |
| Air circulation | Keep air moving around the heat sink. |
| Component temperature | Stay within safe temperature limits. |
Tip: Always check your device’s needs before you choose a heat sink. The right heat sink selection keeps your electronics cool and safe.
You can pick the right heat sink by following some steps. First, look at how air moves around your device. Figure out how big your heat sink should be. Make a checklist to help you. Set the highest temperature your part can handle. Find out how much power turns into heat. Check the thermal resistance numbers. Choose a heat sink that fits in your space. Always read the datasheet for your part. Think about how air and materials affect cooling. You can use guides to learn more about heat sink design. Compare different materials to see what works best. Clean your heat sink often so it keeps working well.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of a heat sink?
You use a heat sink to move heat away from electronic parts. This keeps your device cool. It helps your device work better and last longer.
How do I know if my device needs a heat sink?
You check the power your device uses and the highest temperature it can handle. If your device gets hot during use, you need a heat sink.
Can I use any heat sink for my project?
You should not use just any heat sink. You need to match the size, shape, and cooling ability to your device. Always check the datasheet before you choose.
What happens if I pick the wrong heat sink?
If you choose the wrong heat sink, your device can overheat. This may cause damage or make your device stop working.
Where can I find help with heat sink selection?
You can read datasheets, use online tools, or ask an expert. These resources help you make the best heat sink selection for your project.




