Custom Aluminum Heat Sink Extrusion: Design, Prototyping & Production

Custom aluminum heat sink extrusion helps control heat in machines. It keeps electronics and systems from getting too hot. Custom solutions work well because they match your needs. Most new electronics use extruded heat sinks for good value. When you start a project, think about how much heat there is. Also, think about space and how parts fit together. Special designs and fast prototyping make cooling better. If you want a custom radiator, we can help for free. You just need to send us your drawings.
Key Takeaways
- Custom aluminum heat sinks help control heat in electronics. They keep devices safe and working well.
- Picking the right aluminum alloy, like 6061 or 6063, makes heat sinks work better. These alloys help heat move and last longer.
- Using CAD tools for design and testing finds problems early. This saves time and money when making prototypes.
- Working closely with manufacturers helps make good products. It also lets you get solutions made just for your project.
- Checking quality often during production makes sure heat sinks work well. It also helps them meet industry rules.
Aluminum Heat Sink Extrusion Overview
What Is Aluminum Heat Sink Extrusion
Aluminum heat sink extrusion makes cooling parts for machines. You heat aluminum and push it through a shaped die. This creates long pieces with fins and channels. These fins and channels help move heat away from devices. Extrusion is cheaper and faster than other ways. It also lets you change designs more easily. Look at the table below to see how it compares:
| Feature | Extruded Heat Sinks | Skived Heat Sinks |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Slightly higher thermal resistance due to manufacturing process | Superior due to single-piece construction |
| Surface Area and Cooling Efficiency | Limited fin thickness and spacing reduces efficiency | Thinner, closely packed fins enhance dissipation |
| Customization and Design | Limited by die design | More flexible design options |
| Manufacturing Cost and Scalability | More cost-effective and suitable for high-volume production | More complex and expensive to manufacture |
Benefits of Custom Extrusions
Custom aluminum heat sink extrusion gives you many good things. Aluminum moves heat fast and keeps things cool. It is light, so products are easy to carry. Aluminum costs less and lasts a long time. The extrusion process uses less material and makes less waste. This helps the environment. You can make heat sinks that fit your space and add special features.
- Aluminum heat sinks last long and need less fixing.
- The extrusion process is good for the planet and helps recycling.
- Aluminum has a thermal conductivity of 205 W/mK for moving heat.
- Its light weight is great for planes and portable electronics.
- Custom designs fit your needs and save space.
- You can make tricky shapes fast and save time.
Common Applications
Custom aluminum heat sink extrusion is used in many fields. These heat sinks cool machines, cars, and electronics. The table below shows where they are used:
| Industry |
|---|
| Machinery |
| Automotive |
| Wind Power |
| Construction Equipment |
| Compressors |
| Railway Locomotives |
| Household Appliances |
| Electronics |
You can use these heat sinks in computers and wind turbines. Each job needs a special design to handle heat well. If you want a custom radiator, we can help for free. Just send us your drawings.
Design Factors
Thermal Requirements
When you design a heat sink, think about heat first. The main goal is to keep electronics cool and safe. Aluminum heat sink extrusion works well because fins make more surface area. This helps air move and heat leave faster. Aluminum lets heat travel away quickly. Good design stops overheating and keeps devices working.
- Fins give more surface area for cooling.
- Aluminum moves heat fast to keep things safe.
- Smart design helps electronics last longer.
Pick materials that are light and not expensive. 6000 series alloys like 6061 and 6063 work well. They have thermal conductivity between 166 and 201 W/m•K. Match the material to how much heat your device makes.
- Aluminum is lighter and costs less than copper.
- 6000 series alloys move heat well.
- The material you pick changes how heat leaves in strong electronics.
Custom extruded aluminum profiles let you make special shapes. These shapes help heat leave faster. This is important for power electronics and big machines. Standard heat sinks may not work for these jobs.
Fin Geometry & Base Thickness
Fin geometry is important for cooling. You can pick different fin shapes for your needs. Straight fins work best with fans. Conical fins help with natural convection. The table below shows how fin design changes performance:
| Fin Design | Thermal Performance | Weight Consideration | Airflow Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Straight Fin | Better | Lighter package | Preferred with active cooling |
| Conical Fin | Slight advantage | Heavier | Better for natural convection |
Folded fins give more surface area and use less space. This design lets you add more phase change material. It helps cooling and saves money because it needs less work.
The base thickness matters too. A thick base spreads heat better across the fins. This makes cooling work well. But if the base is too thick, the heat sink gets heavy and costs more. It does not make cooling much better.
Material & Surface Finish
Pick the right aluminum alloy for your heat sink. The most common alloys are 6061 and 6063. These alloys move heat well and are strong. 1050 aluminum moves heat even better, but it is too soft for most uses. The table below compares the alloys:
| Alloy | Thermal Conductivity (W/m•K) |
|---|---|
| 1050 | 229 |
| 6061 | 166 |
| 6063 | 201 |
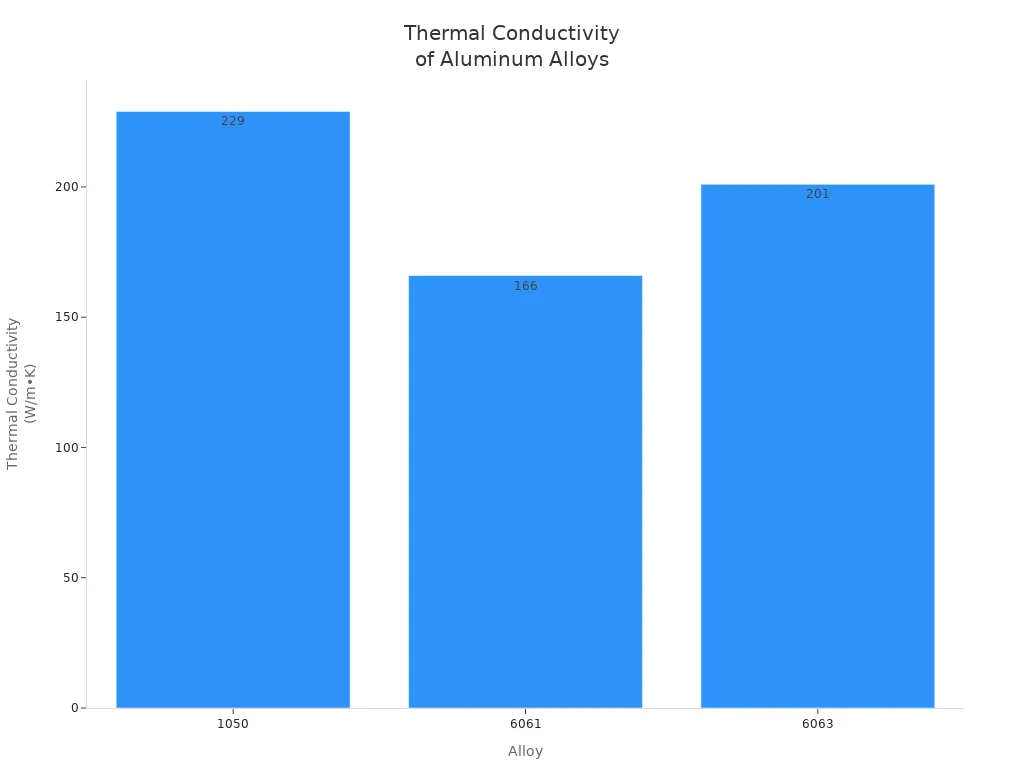
Choose the alloy based on what your project needs. Think about weight, how easy it is to shape, and cost. 6061 and 6063 are popular because they are strong and move heat well.
Surface finish helps protect and makes the heat sink look nice. Anodizing protects the aluminum and looks good. Powder coating adds a strong layer. These finishes do not change how heat moves much. Most heat leaves by convection. The surface should be flat and smooth for good contact with the heat source.
Simulation & CAD Tools
You can use CAD tools to design your heat sink. These tools help you make special shapes and test cooling. Popular software includes Solidworks, ProE, and AutoCAD. For thermal simulation, use Ansys Icepak or Solidworks Flow Simulation.
- Solidworks
- ProE
- AutoCAD
- Ansys Icepak
- Solidworks Flow Simulation
These programs let you model airflow, heat movement, and fin shapes. You can see how your design works before you build it. This helps you avoid mistakes and saves time.
If you want a custom radiator, we can help for free. Send us your drawings to start your project.
Prototyping & Validation
Rapid Prototyping Methods
You need to check if your heat sink design works well. Rapid prototyping lets you do this fast. There are a few ways to make your first sample. Each way has its own good points. The table below shows the main ways to make prototypes for Aluminum Heat Sink Extrusion:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Extrusion | You push aluminum alloys through a die to make long shapes. This is good for heat sinks. |
| CNC Machining | You use computer tools to cut and shape aluminum blocks. This gives very exact results. |
| Die Casting | You melt aluminum and pour it into a mold. This is best for tricky shapes. |
Pick the way that fits your project, money, and time.
Thermal Testing & Simulation
After making a prototype, you need to see how well it cools. You can use different tests to check how the heat sink works and how strong it is. The table below lists common tests for heat sink prototypes:
| Test Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance/ΔT Testing | You measure how much the temperature goes up with heat. This shows how well it cools. |
| Mechanical Inspection | You check if the heat sink is strong and matches your plan. |
| Environmental Stress Tests | You test the heat sink with hot, cold, and shaking to see if it lasts. |
| Airflow or CFD Correlation Tests | You compare real cooling results with computer tests. |
These tests help you make sure your design works before making many.
Iterative Refinement
You might need to change your design after testing. You can change fin shapes, base thickness, or surface finish to get better results. You keep making and testing new samples until you reach your goal. This helps you find problems early and save money.
Tip: You can make your heat sink better by making small changes and testing again. This helps your heat sink work well.
We can help you make your radiator and give a free check. Please send us your drawings to start.
Production Steps

Extrusion & Cutting
First, you make a detailed design. Engineers use CAD software to plan each part. They run simulations to check the design. Next, technicians create the die. They pick the right steel and cut it with CNC machines. The die is heat treated to make it strong. You get high-quality aluminum billets and heat them up. The extrusion process pushes the hot billet through the die. This forms the custom shape. Cooling keeps the shape steady. Stretching makes the profile stronger and helps find defects. Automated saws cut the profiles to the right length. Surface finishing like anodizing gives the heat sink its final look and protects it.
Main Steps in Extrusion & Cutting:
- Design and Engineering
- Die Creation
- Billet Preparation
- Extrusion Process
- Stretching
- Cutting
- Surface Finishing
This process makes sure your Aluminum Heat Sink Extrusion fits your needs and works well.
CNC Machining & Secondary Operations
CNC machining gives your heat sink high precision. You can reach accuracy up to ±0.01mm. This lets you make microchannel structures as thin as 0.3mm. These thin channels help heat leave faster, up to 30% better. You can also get tolerances of ±0.025mm. This makes it possible to create complex shapes. Quality checks look at every part for size and smoothness.
After extrusion, you need more steps to finish the heat sink. These steps include:
- Drilling
- Cutting to final length
- Machining holes or pockets
- Stamping
- Anodizing
- Painting
These steps add holes, special features, or surface treatments. They make your heat sink ready to use.
Tip: Use CNC machining for parts that need tight sizes or special shapes. This helps your heat sink fit well and work better.
Surface Treatments
Surface treatments protect your heat sink and help it work better. Anodization makes a porous layer that helps heat leave faster. This layer also protects aluminum from water and chemicals. It makes the heat sink last longer in tough places. Black anodizing raises emissivity, which helps with cooling by radiation. Chromate conversion coatings give some protection from rust and do not change thermal performance much.
| Surface Treatment | Corrosion Resistance Effect | Thermal Performance Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Anodizing | High | Slight drop in thermal conductivity (1-3%), but raises emissivity by up to 80% |
| Black Anodizing | Very High | Raises emissivity to 0.8-0.9, good for radiation cooling |
| Chromate Conversion Coatings | Moderate | Little effect on thermal performance |
Pick the surface treatment that fits your needs. Anodized heat sinks last longer and keep working in hard conditions.
Quality Control
Quality control makes sure your heat sink is safe and works well. You check raw materials to see if the aluminum is right. You watch the extrusion process to keep it steady. You check the size of each profile to match the design. You look for defects on the surface. You test strength and durability. You check packaging to make sure products arrive safely.
Standard Quality Control Measures:
- Raw material inspection
- Extrusion process control
- Profile dimension checks
- Surface quality assessments
- Mechanical properties testing
- Final packaging inspection
You get a heat sink that meets your needs and works well in real life.
We can help you make your radiator and give a free check. Please send us your drawings to start.
Project Tips
Manufacturer Collaboration
You should work with your manufacturer from the start. Pick a partner who knows a lot about custom heat sink design. They should have a good history of making these products. Talking often helps fix problems fast. Good manufacturers use strong quality checks and new technology. They help you pick the best materials for your project. The table below lists important things to look for:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Technical Expertise | Ability to design high-performance products and customize solutions for your needs. |
| Quality Control | Strict measures ensure reliable and consistent thermal performance. |
| Material Selection | The right materials improve thermal conductivity and product strength. |
| Manufacturing Technologies | Advanced processes deliver quality and timely products. |
| Communication | Clear updates and support keep your project on track. |
Design Optimization
You can save money and cool better by changing your design. For example, a company needed to cool 5G equipment. Their first idea used a big 10-inch heat sink. Tests showed it did not fit well. They changed to two 5-inch profiles with better fins. This kept cooling the same and saved 15% on materials. Always try to balance cooling with easy installation. Change fin shapes and width to fit your needs.
Tip: Try out different designs early. Small changes can help lower costs and improve how well it works.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Many projects have problems you can stop before they happen. Here are the most common mistakes:
- Picking a heat sink that is too small or has too little surface area.
- Using fins that are too close together, which blocks airflow.
- Not thinking about how air moves around the fins or putting them the wrong way.
- Making bad mounting surfaces, which makes it harder for heat to leave.
- Adding features that are hard to make, which slows down production.
Check each step to stop these problems.
Documentation Best Practices
Good records help your project do well. You should track materials, sizes, and test results. Use clear notes for checks and certifications. The table below shows the best ways to keep records:
| Documentation Practice | Purpose | Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Material Inspection | Confirm thermal conductivity and strength | Certification, strength and conductivity tests |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Ensure correct sizes | CMM, visual checks |
| Thermal Performance Testing | Measure cooling ability | Thermal tests, CFD simulations |
| Flow Testing | Check airflow and cooling | Wind tunnel, fan tests |
| Integration and Mounting Tests | Verify fit and mounting | Fit tests, TIM testing |
| Reliability Testing | Test long-term durability | Thermal cycling, vibration tests |
| Compliance and Certification | Meet industry standards | Certification, test records |
| Post-Production Inspection | Final quality check | Visual inspection, packaging checks |
You can contact us to make your own radiator and get a free check. Please send us your drawings to begin.
You follow many steps to make Aluminum Heat Sink Extrusion. First, you get the billet ready. Then, you finish the heat sink. Simulation and validation help you guess how well it cools. They also help you avoid expensive mistakes.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Simulation | CFD software checks airflow and heat before making the part. |
| Validation | Early tests show if your design keeps things cool. |
Custom heat sinks help devices last longer. They move heat away fast and stop rust.
- You get solutions made just for you.
- Devices work well and stay cool for a long time.
To begin, decide what you need. Pick the most important features. Work with experts from the start. Our team can help you make aluminum radiators and check them for free. Send us your drawings to get started.
Pick an alloy by looking at how well it moves heat, how strong it is, and how much it costs. Alloys like 6061 and 6063 are good for most electronics. If you want even better heat movement, try 1050. But 1050 is softer than the others.
It usually takes 2 to 6 weeks to make a custom heat sink. The time can change if the design is hard or if you need many pieces. Talking early with your manufacturer can help things go faster.
Yes, you can pick anodizing, powder coating, or chromate conversion coatings. These treatments help stop rust and make the heat sink look better. Black anodizing also helps with cooling by raising emissivity.
You need to send detailed CAD drawings. Use formats like STEP, DXF, or DWG. These files help engineers see what you want and make the right prototype.



