what is water cooling block?
A water cooling block is a custom heat sink that uses liquid to pull heat away from your computer’s parts. You place it on top of a CPU or GPU, and it transfers heat to the coolant flowing inside. This method works much better than air cooling. A Liquid cold plate can be 4-5 times more efficient than a standard fan. You get lower temperatures and more reliable performance.
- Water cooling block moves heat faster than air.
- Microfins inside help absorb heat quickly.
Key Takeaways
- A water cooling block pulls heat away from your CPU or GPU using liquid, cooling your PC much better than air fans.
- Microchannels and microfins inside the block increase heat transfer by giving coolant more surface to absorb heat quickly.
- Water blocks keep your computer cooler, quieter, and more stable, helping your hardware last longer and perform better.
- Choose a water block that fits your CPU or GPU model and motherboard, and follow installation guides carefully for best results.
- Custom water cooling loops offer more control and better cooling, while AIO units are easier to install but less flexible.
Purpose
Main Function
When you use a water cooling block in your PC, you give your computer a powerful way to stay cool. The main job of this block is to move heat away from important parts like your CPU or GPU. Here’s how it works:
- The copper base of the block sits right on top of the part that gets hot, like your CPU.
- Inside the block, tiny channels called micro-channels increase the area that touches the coolant.
- Coolant flows through these channels and picks up the heat.
- The warm coolant then leaves the block and heads to the radiator, where it cools down before coming back.
Think of the water cooling block as the first line of defense against overheating. It grabs the heat fast and sends it away, so your computer can keep running smoothly.
Key Roles
A water cooling block does more than just cool your PC. It helps your whole system stay stable and work better. Here are some of the key roles it plays:
- It keeps your CPU and GPU at safe temperatures, even when you play games or run heavy programs.
- It helps your computer run quietly because you don’t need loud fans spinning all the time.
- It protects your hardware from damage caused by too much heat.
- It helps your system stay stable by keeping the temperature steady, which means fewer crashes or slowdowns.
- It supports the balance of water movement inside the block, which can affect how well your computer parts work together.
When you use a water cooling block, you give your PC a better chance to last longer and perform at its best.
How It Works
Heat Transfer
When you use a water cooling block, you tap into some cool science. The block sits right on top of your CPU or GPU. It grabs heat from the chip and moves it into the coolant. This process uses two main ideas: conduction and convection.
Contact Surface
The base of the block touches the hot part of your computer. Heat travels from the chip into the metal base. This is called conduction. The metal, usually copper, pulls heat away fast because it has high thermal conductivity. The heat moves through the solid metal, following a rule called Fourier’s law. The bigger the temperature difference, the faster the heat moves.
Coolant Flow
Once the heat reaches the inside of the block, the coolant takes over. The liquid flows through tiny channels and carries the heat away. This is convection. Pumps push the coolant through the block, so the hot liquid leaves and cooler liquid comes in. The water keeps moving, so your computer stays cool.
Tip: The faster the coolant moves, the better it can grab heat and carry it away.
Microfin arrays and jetplates make this process even better:
- Microfin arrays have lots of thin channels, usually about 0.6 mm wide. These channels give the coolant more surface to touch, so it can pick up more heat.
- Jetplates force the water to move quickly and create turbulence. This means the water mixes up and doesn’t leave any spots untouched.
- When you combine microfins and jetplates, you get maximum surface area and strong mixing. This helps your water cooling block work at top speed.
- Jetplates can make the flow harder for pumps, so designers balance performance and flow resistance.
- Some blocks use direct cooling with jetplates, but sealing and dead zones can be tricky.
System Integration
You can use water blocks in two main types of cooling systems: custom loops and AIO (All-In-One) units.
Custom loops let you pick each part. You choose your water cooling block, pump, tubes, and radiator. You can match blocks to your CPU, GPU, or even RAM. Some brands make blocks that fit certain models, so installation is easier. Push-in fittings and pre-cut tubes help you set up your loop without cutting or threading tubes yourself. You can swap out parts or add new ones whenever you want.
AIO systems come as sealed units. The pump and water block are built together. You can’t add more parts or change the setup. The pump is made for just that loop, so it isn’t strong enough for extra radiators or blocks. If you try to expand an AIO, you might break the pump or lose your warranty. AIOs are simple and quick to install, but you lose the chance to customize.
Note: Custom loops give you more control and better cooling, but AIOs are easier for beginners.
Components

Base Plate
The base plate sits right on your CPU or GPU. This part touches the chip and pulls heat away fast. You want a base plate that can move heat quickly, so the material matters a lot.
Materials
Here’s a quick look at the most common materials you’ll find in water block base plates:
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | ~400 | Excellent thermal conductivity, heavy, expensive, ideal for high heat flux applications |
| Aluminum (Al) | ~205 | Lightweight, cost-effective, lower thermal conductivity, prone to corrosion |
| Stainless Steel | 15-45 | Lower thermal conductivity, excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for harsh environments |
| Composite | Varies | Combination of metals, ceramics, carbon materials for tailored properties |
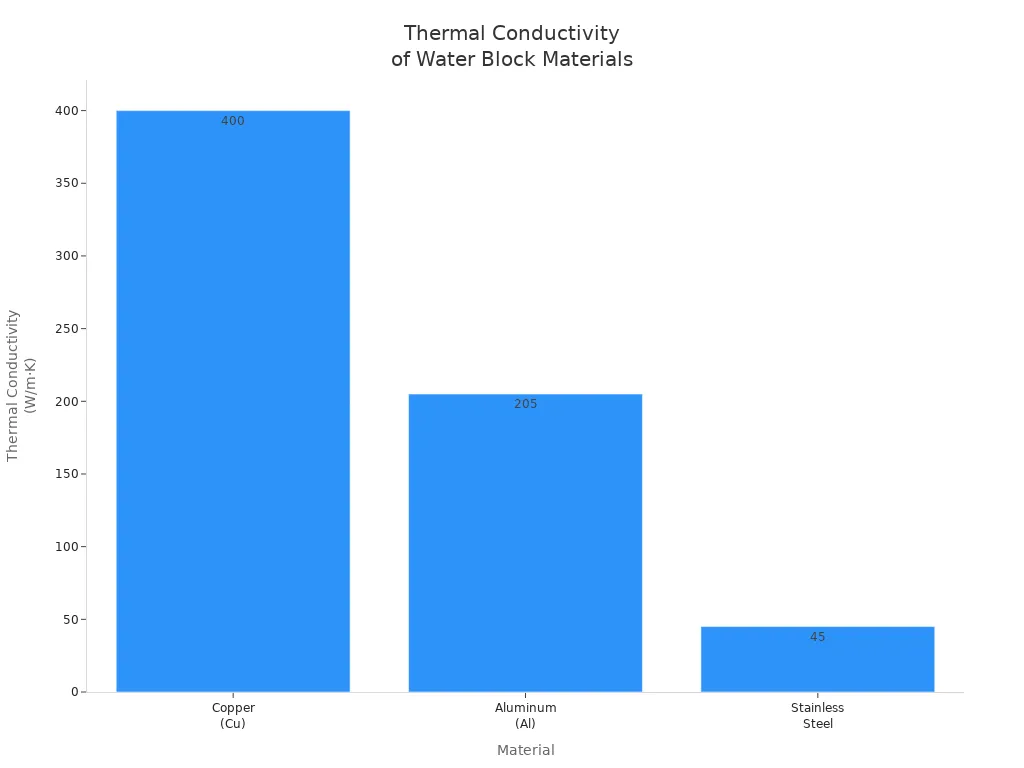
- Copper gives you the best heat transfer. It’s strong and lasts a long time, but it costs more and can tarnish.
- Aluminum feels lighter and costs less. It doesn’t move heat as well and can corrode if you don’t take care of it.
Microfins
Microfins look like tiny metal blades inside the block. They create lots of small paths for water to flow through. This design gives the coolant more surface to touch, so it grabs more heat from the base plate. You get better cooling because the heat moves from the metal to the water faster. Most microfins use copper or aluminum, which helps pull heat away even more.
Tip: Microfins make a huge difference in how well your water block cools your PC.
Top Cover
The top cover keeps everything inside the block safe. It also makes your setup look cool. Many covers use a mirror finish, so RGB lights shine through and show off logos or colors. The cover doesn’t help with cooling, but it protects the block and adds style to your build.
Ports and Seals
You’ll find two main ports on every water block—one for coolant to enter and one to leave. These ports connect to your tubes. Good seals stop leaks and keep your system safe. Most blocks use rubber or silicone gaskets to make sure water stays where it should.
Extra Features
High-end water blocks come with some awesome extras:
- RGB lighting you can control with software
- Clear acrylic tops to show off the coolant or solid black tops for a stealthy look
- Nickel plating on copper for extra protection against corrosion
- Built-in temperature sensors and even LCD screens to show real-time info
- Central inlet designs and super-fine micro-channels for better cooling
- Options that fit both AMD and Intel CPUs
You can pick the features that match your style and needs. Some blocks focus on looks, while others give you more control or better performance.
Water Cooling Block Types
CPU Blocks
You will find CPU blocks as the most common type of water cooling block. These blocks sit right on top of your processor. They pull heat away from the CPU and send it into the coolant. Most CPU blocks fit popular Intel and AMD platforms, like Z690, Z790, X670, and X670E. Brands such as EKWB and Watercool make blocks that match these sockets. You just need to check your motherboard and CPU model before you buy.
GPU Blocks
GPU blocks cool your graphics card. Some cover only the GPU chip, while others are full-cover blocks. Full-cover blocks cool the GPU, memory chips, and VRMs all at once. This design helps your graphics card run cooler and more stable. You can find blocks for top GPUs like NVIDIA RTX 4090, 4080, and AMD Radeon RX 7900 XT. Popular models include the EKWB EK-Quantum Vector and Aquacomputer Kryographics Next RTX.
Tip: Full-cover GPU blocks fit only certain card layouts, so always check your exact GPU model.
RAM & VRM Blocks
RAM and VRM blocks are less common, but you might want them if you overclock or want a showpiece PC. RAM blocks cool your memory sticks, mostly for looks or extreme builds. VRM blocks cool the voltage regulators near your CPU. Some motherboards even offer monoblocks, which cool both the CPU and VRMs together. You need to match these blocks to your motherboard and RAM for a good fit.
| Component | Purpose | Design Characteristics | Mounting Considerations | Cooling Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Water Block | Cool the CPU | Fits CPU heat spreader and socket | Designed for CPU socket area | CPU die and heat spreader |
| GPU Water Block | Cool GPU, RAM, VRMs | GPU-only or full-cover (GPU+RAM+VRMs) | Fits GPU PCB layout | GPU, RAM, VRMs |
| VRM Water Block | Cool voltage regulators | Size/shape varies, adjustable brackets | Matches VRM array and mounting holes | VRMs near CPU |
| RAM Water Block | Cool memory modules | Needs special mounting, replaces stock heat spreaders | Attaches to RAM modules | RAM modules |
| Monoblock | Cool CPU and VRMs (sometimes chipset) | Oversized, motherboard-specific | Designed for specific motherboard models | CPU, VRMs, sometimes chipset |
Universal vs. Specific
You can pick between universal and component-specific water cooling blocks. Universal blocks fit many GPUs and use flexible mounting. They cool only the GPU chip, so you need extra heatsinks for memory and VRMs. These blocks are easy to install and may fit future upgrades. Full-cover or specific blocks fit only one card or motherboard. They cool everything—GPU, RAM, and VRMs—but you cannot reuse them on a different model. Installation takes more time and care.
- Universal blocks: fit many cards, cool only the GPU die, need extra cooling for other parts.
- Full-cover blocks: fit one card, cool GPU, RAM, and VRMs, best for performance.
AIO Water Cooling Block
AIO (All-In-One) water cooling blocks come as sealed kits. You get a pump, radiator, and block in one package. These blocks are easy to install and need little upkeep. They work well for most users and come with warranties. You cannot add more parts or change the setup. Custom loops let you cool both CPU and GPU, but they take more work and cost more. AIOs give you better cooling than air, but custom loops win if you want the best performance and full control.
Benefits
Performance
You want your PC to run fast and stay cool, right? Water blocks help you get there. When you use liquid cooling, your system can handle more heat. This means you can play games, edit videos, or render graphics without worrying about your CPU or GPU slowing down. Here’s what you get with water blocks:
- Stable temperatures, even during heavy gaming or rendering.
- Higher overclocking potential, so you can push your hardware further.
- No thermal throttling, which means your CPU and GPU keep their top speeds.
- Radiators move heat out of your case quickly, keeping everything inside cooler.
- Flexible radiator placement lets you optimize airflow and cooling.
Gamers and PC enthusiasts love water blocks because they keep performance high and temperatures low. You can enjoy smoother gameplay and better reliability every time you use your computer.
Noise Reduction
Nobody likes a noisy PC. Water blocks make your system quieter by letting fans run slower. Since liquid cooling pulls heat away more efficiently, your fans don’t need to work as hard. Take a look at this comparison:
| Cooling Type | Noise Level (dBA) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Air Cooling | 46 | Fans run at high speed under load, producing more noise |
| Water Cooling | 40 | Fans run at lower speeds due to efficient heat transfer via water blocks and radiators, reducing noise by about 6 dBA |
You’ll notice the difference right away. Your PC sounds calmer, even when you’re gaming or working hard. Less noise means you can focus better and enjoy your setup more.
Longevity
You want your computer to last as long as possible. Water blocks help with that, too. By keeping your CPU, GPU, and other parts cooler, you reduce the risk of overheating. Lower temperatures mean less stress on your hardware. Here’s how water blocks help:
- They prevent thermal throttling and overheating.
- Your components run cooler, which extends their lifespan.
- Stable temperatures protect your PC during long gaming or editing sessions.
- Consistent cooling keeps your hardware reliable for years.
Tip: If you want your PC to stay fast and last longer, water blocks are a smart choice.
Choosing One
Compatibility
When you pick a water cooling block, you want to make sure it fits your system. You need to check a few things before you buy:
- Look at your CPU socket type. Some blocks fit many Intel sockets, like the 1150 series, because they share the same mounting system.
- Check your motherboard layout. Sometimes, big heat sinks or other parts near the CPU can block the water cooling block from fitting.
- Always check the manufacturer’s compatibility list. This helps you see if the block matches both your CPU socket and motherboard.
- Pay attention to mounting systems. Intel and AMD use different clips and backplates, so you may need to remove or swap them.
- Make sure you have enough space around the CPU socket. Some motherboards have extra parts that can get in the way.
Tip: Follow the installation guide closely. Clean your CPU, use the right amount of thermal paste, and secure the block with the hardware provided.
Materials
You might wonder which material works best for your water cooling block. Copper has high thermal conductivity, but in real PC setups, the difference between copper and aluminum is only a few degrees. The coolant limits how much heat can move, not just the metal. Mixing copper and aluminum in the same loop can cause corrosion, so stick with one type. Acrylic and acetal are used for the top cover. Acrylic looks cool with lighting, but it can crack. Acetal is tough and resists chemicals, but it’s not see-through.
| Material | Cooling | Durability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Best | Strong | Avoid mixing with aluminum |
| Aluminum | Good | Strong | Use only with aluminum parts |
| Acrylic | None | Brittle | Great for lighting effects |
| Acetal | None | Durable | Opaque, tough |
Features
If you want top performance, look for these features:
- Make sure the block fits your CPU socket. Most brands include adapters for different sockets.
- Choose a block with a copper base for better heat transfer.
- Look for microchannels inside the block. These help the coolant grab more heat and keep your CPU cool.
You can also find blocks with RGB lighting, clear tops, or built-in sensors. Pick what matches your style and needs.
Are water blocks compatible with all CPUs and GPUs?
Water blocks are not universal. CPU blocks depend on the socket type and motherboard layout. Some fit many sockets, but you must check for space and mounting. GPU blocks come in two types. Universal blocks fit many cards but cool only the GPU chip. Full-coverage blocks cool more parts but fit only specific cards. Always check the compatibility list before you buy.
What is a water block in a computer cooling system?

A water block is a key part of a liquid cooling system for your PC. You place it right on top of your CPU or GPU. It pulls heat away from these parts and sends it into the coolant. The coolant then carries the heat to a radiator, where fans blow it out of your case. This setup keeps your computer running cool and quiet, even when you push it hard.
How does a water block work in a liquid cooling setup?
You start by mounting the water block directly onto your CPU or GPU. You use thermal paste to help transfer heat from the chip to the block’s metal base. The water block absorbs the heat and passes it to the liquid flowing inside. A pump moves this warm liquid to a radiator, where fans cool it down. The cooled liquid then returns to the block, ready to grab more heat. This cycle keeps your PC at safe temperatures, even during heavy gaming or editing.
Tip: Liquid cooling works better than air because water can carry more heat away from your parts. You get lower temps and less noise.
What components can a water block cool in a PC?
You can use water blocks to cool several parts inside your computer. Here’s a quick look:
| PC Component | Can you cool it with a water block? | Why use it? |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | ✅ | Keeps your processor cool and stable |
| GPU | ✅ | Stops your graphics card from overheating |
| VRMs | ✅ | Protects voltage regulators for longer life |
| Chipsets | ✅ | Helps your motherboard run more reliably |
Water blocks often use copper or aluminum for better heat transfer. Some even have RGB lights to make your build look awesome.
Why use a water block instead of traditional air cooling?
You get several big benefits when you pick a water cooling block over a regular air cooler:
- You enjoy better cooling, which means higher speeds and more stable performance.
- Your PC runs quieter because fans don’t need to spin as fast.
- You can overclock your CPU or GPU without worrying about overheating.
- The system looks cleaner and more stylish, especially with custom lighting.
- Liquid cooling handles hot rooms better than air cooling.
If you want a cooler, quieter, and better-looking PC, a water cooling block is a smart choice.
A water block sits right on your CPU or GPU and starts the cooling process by pulling heat into the liquid. You get better performance, less noise, and longer-lasting parts when you use one. Before you buy, always check your exact GPU or CPU model and use brand tools to find the right fit. If you plan ahead and match your parts, your PC will stay cool and run strong for years.
FAQ
What happens if my water block leaks?
If your water block leaks, you might see water on your PC parts. Turn off your computer right away. Dry everything with a towel. Let it sit for a day. Check for damage before turning it back on.
Can I install a water block by myself?
Yes, you can! Most water blocks come with clear instructions. You just need a screwdriver and some patience. If you follow the guide, you should finish in about an hour.
Do I need to clean my water block?
You should clean your water block every 6 to 12 months. Dust and gunk can build up inside. Cleaning keeps your cooling strong. Use distilled water or a special cleaner for best results.
Will a water block make my PC quieter?
Yes! Water blocks help your PC run cooler, so your fans spin slower. You get less noise and a more peaceful workspace. Many gamers and creators love this quiet upgrade.
Can I use any coolant with my water block?
You should use coolant made for PC water cooling. Tap water can cause corrosion or algae. Coolant from the store protects your parts and keeps your system running smooth.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.




