Aluminum heat sink extrusions

Aluminum heat sink extrusions help control heat in electronics. Devices can break if they get too hot. In fact:
Temperature causes more than half of device failures.
Good heat dissipation keeps electronics safe and working. Many makers choose aluminum, especially alloys like 6063-T6. Aluminum has great thermal conductivity and is easy to shape. Electronics are getting smaller and stronger. This makes more industries want aluminum heat sink solutions.
Key Takeaways
Aluminum heat sink extrusions help cool electronics. They stop devices from getting too hot. This helps devices last longer.
Picking the right aluminum alloy is important. Alloys like 6063-T6 are strong and conduct heat well. This helps move heat away from parts.
The shape of the fins and the size of the surface matter a lot. These features change how well the heat sink cools.
You can customize heat sinks for different devices. This means you can make them fit special cooling needs.
Picking and installing the right heat sink is important. It helps devices work better and last longer. That is why heat sinks are used in many industries.
What is an aluminum heat sink extrusion
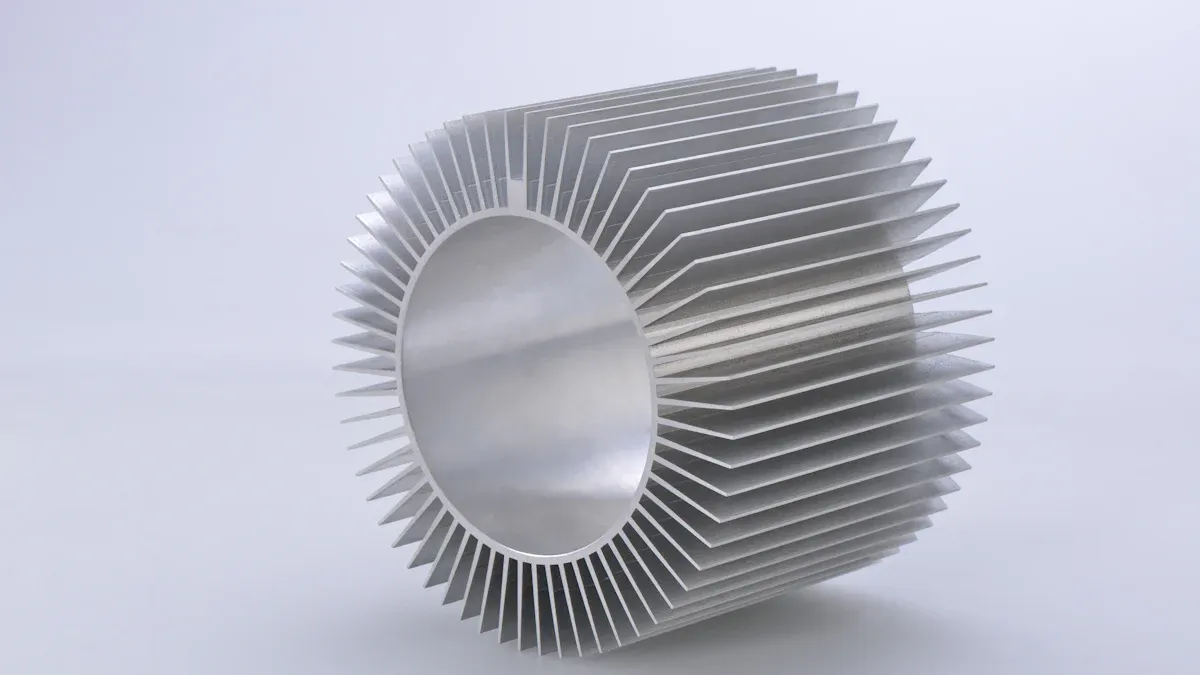

Structure and function
An aluminum heat sink extrusion is a special part made from aluminum. You use it to help cool down electronics and machines. The main job of a heat sink is to move heat away from important parts. This helps your devices stay safe and last longer. When you look at a heat sink, you see many thin fins or ridges. These fins increase the surface area, so more heat can escape into the air.
Heat is the enemy of efficiency. To extract heat from lighting, from electronics and circuit boards, engineers design a heat sink to conduct the heat, and utilize high surface area fins to allow the heat to convect away from the product.
You can find heat sink extrusions in many shapes and sizes. Some are small for tiny gadgets. Others are big for powerful machines. Here are some common features you might notice:
Cross-sectional profiles: These can be rectangular, square, round, or even hexagonal.
Hollow shapes: Some heat sinks look like tubes.
Wall thickness: Thicker walls give more strength.
Length: You can get standard or custom lengths.
Tolerances: These make sure the heat sink fits your device just right.
The way a heat sink is built changes how well it works. Three things matter most:
Fin geometry: The shape and spacing of the fins help move heat faster.
Surface area: More surface area means better cooling.
Airflow channels: Good spacing lets air move easily, which helps cool your device.
A heat sink works as a passive heat exchanger. It takes heat from your device and moves it to the air around it. This keeps your electronics at a safe temperature.
Common aluminum alloys
You have many choices when picking the right aluminum for your heat sink. Some alloys work better than others. The most popular ones are 1050, 6060, 6061, and 6063. Each alloy has its own strengths.
Aluminum Alloy | Thermal Conductivity (W/m•K) |
|---|---|
1050 | 229 |
6060 | 166 |
6061 | 152 |
6063 | 201 |
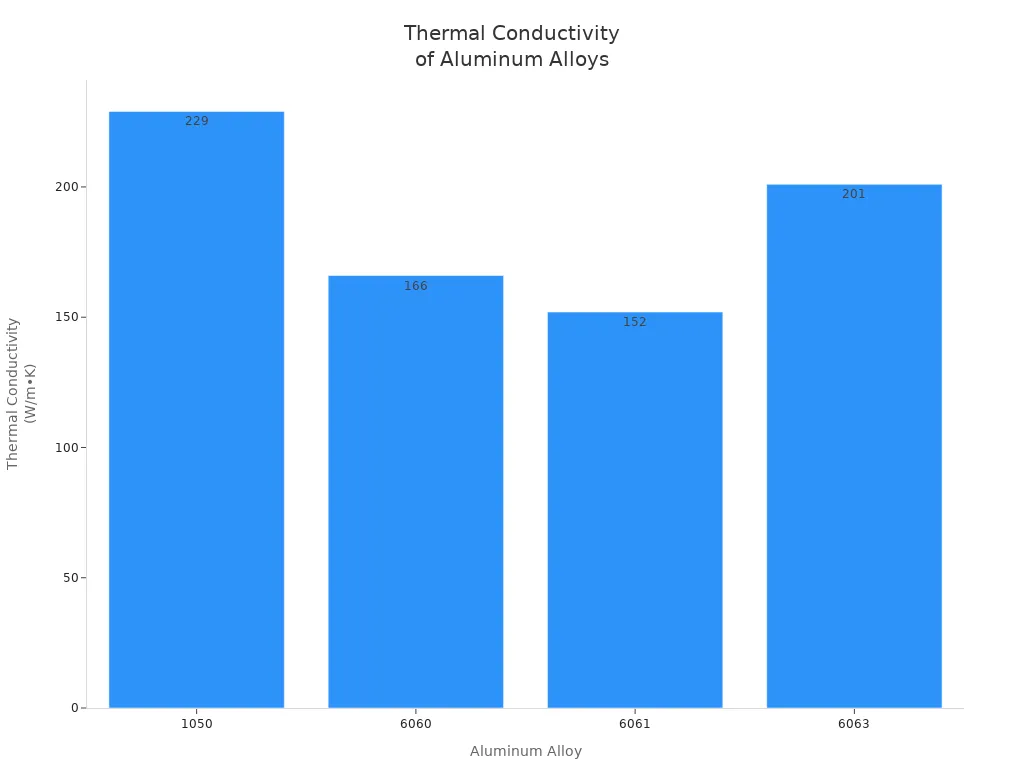
Alloy 1050 has the highest thermal conductivity. This means it moves heat very well. However, it is soft and not strong enough for most heat sink shapes. The 6000 series alloys, like 6060, 6061, and 6063, are stronger and easier to shape. They are perfect for making heat sinks that need to be both tough and good at moving heat.
6063-T6 is a favorite for many engineers. It has a good balance of strength, thermal conductivity, and finish quality. You can shape it into many designs, and it looks smooth when finished. This makes it a top choice for most aluminum heat sink extrusions.
Tip: When you choose an alloy, think about both how well it moves heat and how strong it needs to be for your project.
Heat sink features
Thermal conductivity
You want your electronics to stay cool. Aluminum heat sink extrusions help move heat away fast. Alloys like 6063-T6 and 1050 transfer heat quickly. Copper is even better at moving heat. But copper is heavier and costs more money. You can compare the materials in this table:
Material | |
|---|---|
Aluminum (various alloys) | 136 – 205 |
Copper | 390 – 400 |
Most aluminum heat sink extrusions use alloys with conductivity between 150 and 218 W/m·K. This makes them a smart choice for many devices.
Lightweight and corrosion resistance
Aluminum heat sinks are light and easy to carry. Aluminum has a low density of about 2.7 g/cm³. This means it does not add much weight to laptops or phones. You can install and move them without trouble.
Aluminum does not rust easily. It forms a natural oxide layer that protects it. This layer keeps the heat sink strong, even in wet or rough places. Your heat sink will last a long time.
Tip: Pick aluminum if you want a heat sink that is light and lasts long.
Design flexibility
Aluminum heat sink extrusions come in many shapes and sizes. Makers offer straight fin designs and different profiles. You can choose the right one for your project. Here are some common design options:
Design Option | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Fin Designs | Different shapes and sizes for more surface area | Better heat transfer |
Surface Treatments | Extra coatings for more protection | Longer life in tough environments |
Active Cooling | Uses fans or pumps | Faster cooling |
Passive Cooling | Uses natural airflow | Simple and low cost |
Liquid Cooling | Uses liquid for heat transfer | Great for high-power devices |
Air Cooling | Uses fins and air | Works for most electronics |
You can always find a heat sink extrusion that fits your needs. It works for simple or advanced cooling.
Manufacturing process
Extrusion steps
You can make aluminum heat sink extrusions by following a few steps. Workers start by cutting aluminum ingots into billets. They clean the billets and heat them to about 900°F. This makes the metal soft and easy to shape. Next, the hot billet goes into a hydraulic press. The press pushes the billet through a steel die. The die shapes the aluminum into fins or channels. The new profile comes out very hot. Fans or water sprays cool it down fast. Cooling helps keep the metal strong and straight. Workers then cut the extrusion to the right length. They may also straighten it and age it for hardness like T5 or T6.
Tip: The temperature during extrusion is usually between 800°F and 925°F. Hydraulic rams use strong pressure to push aluminum through the die.
Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
Temperature | 800-925°F (427-496°C) |
Pressure | Hydraulic ram |
Customization options
You can ask for special shapes and sizes for your aluminum heat sink. Makers use special tools to make sure each piece fits your needs. They use statistical process control to keep every extrusion the same size and shape. This helps your heat sink work well every time. CNC machining gives smooth finishes and exact cuts. Machines follow instructions to match your design. Surface treatments like anodizing add protection and make it look better.
Note: Customization lets you pick the number of fins, thickness, and length. You can also choose special coatings for better performance in tough places.
Careful extrusion steps and advanced customization give you a reliable product. This helps your heat sink work well and last a long time.
Applications and selection
Industries and devices
Aluminum heat sink extrusions are used in many industries. These parts help keep things cool and safe. You can find them in lots of places. For example, laptops and gaming consoles use them to stop processors from getting too hot. Computers and servers need them to cool CPUs and GPUs when working hard. Cars use them in engine control units, LED headlights, and power inverters for electric vehicles. They help control heat in these systems. Factories use them in power supplies, motor drives, and machines for automation. These parts help the machines work well. Cell towers and network equipment use them for cooling without fans. Medical devices, like diagnostic tools and imaging systems, need them to keep the right temperature. Many different fields use aluminum heat sinks to protect important electronics.
Choosing the right heat sink
Picking the best aluminum heat sink extrusion takes some thinking. You have to match the heat sink to your device. There are a few things you should think about. Devices that make more heat need bigger heat sinks. The heat sink must fit inside your device and not block other parts. Good airflow helps the heat sink work better. The design should let air move easily. Aluminum is good because it moves heat fast. If the room is hot, you might need a bigger heat sink. Devices that use more power get hotter, so they need better cooling.
Tip: Always check how much heat your device makes before you pick a heat sink. This helps stop overheating.
You also need to think about how to attach the heat sink. There are different ways to mount it. Each way has its own strengths. Here is a table to help you compare:
Mounting Method | Description | Strength/Notes |
|---|---|---|
Screws | Strong and reliable | Needs hole prep and torque control. |
Spring Clips | Fast and low stress | Needs space and preload tuning. |
Push Pins | Quick, tool-less | Limited strength. |
Rivets | Permanent, strong | Not serviceable. |
Thermal Adhesive | Clean, no screws | Permanent, weaker bond. |
Thermal Tape | Easy to use | Weakest under load or vibration. |
Standoffs + Screws | Strong, modular | More complex, space needed. |
You should also choose between natural or forced air cooling. Natural cooling uses air from the room. Forced air cooling uses fans to blow air over the heat sink. Forced air is better for very hot devices.
When you think about all these things, you can pick the right aluminum heat sink extrusion. This will help your device stay cool and last longer.
Aluminum heat sink extrusions help electronics stay cool and safe. Picking the best alloy and design helps your device last longer. The 6000 series alloys, like 6063-T5, are strong and easy to shape. Aluminum is good for the environment because you can recycle it. Recycling aluminum helps cut down on waste.
Benefit | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
High recyclability | Uses less energy and lowers pollution |
Custom designs | Fits your device and cools it better |
Strong and lightweight | Simple to install and move |
Think about what your device needs. Set your cooling goals and check your space. The right heat sink helps your device work well.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of an aluminum heat sink extrusion?
You use an aluminum heat sink extrusion to move heat away from electronic parts. This helps your device stay cool and work longer.
How do you choose the right size heat sink?
You look at how much heat your device makes. Bigger devices or those that get hotter need larger heat sinks with more surface area.
Can you paint or coat an aluminum heat sink?
Yes! You can use anodizing or special coatings. These protect the surface and can help with heat transfer. Always pick a coating that does not block heat flow.
Why do most heat sinks use aluminum instead of copper?
Aluminum is lighter than copper.
It costs less.
You can shape it more easily.
Copper moves heat faster, but aluminum gives you a good balance of cost, weight, and performance.


