Everything You Need to Know About Water Cooling Plates

A water cooling plate helps cool electronic devices by taking heat away from key parts. Coolant moves through the plate’s channels, so it picks up heat and takes it out. This works better than air cooling, so you can get rid of more heat and save energy. Today’s electronics need good thermal management to stop overheating and device damage. Cooling Source has advanced options, so you can pick the best water cooling plate for your needs.
Key Takeaways
- Water cooling plates help take away heat from electronics. This helps devices work better and last longer. Copper plates move heat the best. Aluminum plates are lighter and cost less. The way coolant channels are made changes how well heat leaves. More channels help cool things better. Using the right coolant, like deionized water, stops damage. It also helps cooling work well. You need to check for leaks and clean the system often. This keeps your cooling system working right. Water cooling plates make less noise than air cooling systems. This makes them good for gaming and strong computers. Custom water cooling plates can be made for special devices. This gives the best cooling for each device. Pick the right water cooling plate for your device. Think about how much heat it makes, its size, and how much cooling it needs.
What Is a Water Cooling Plate?
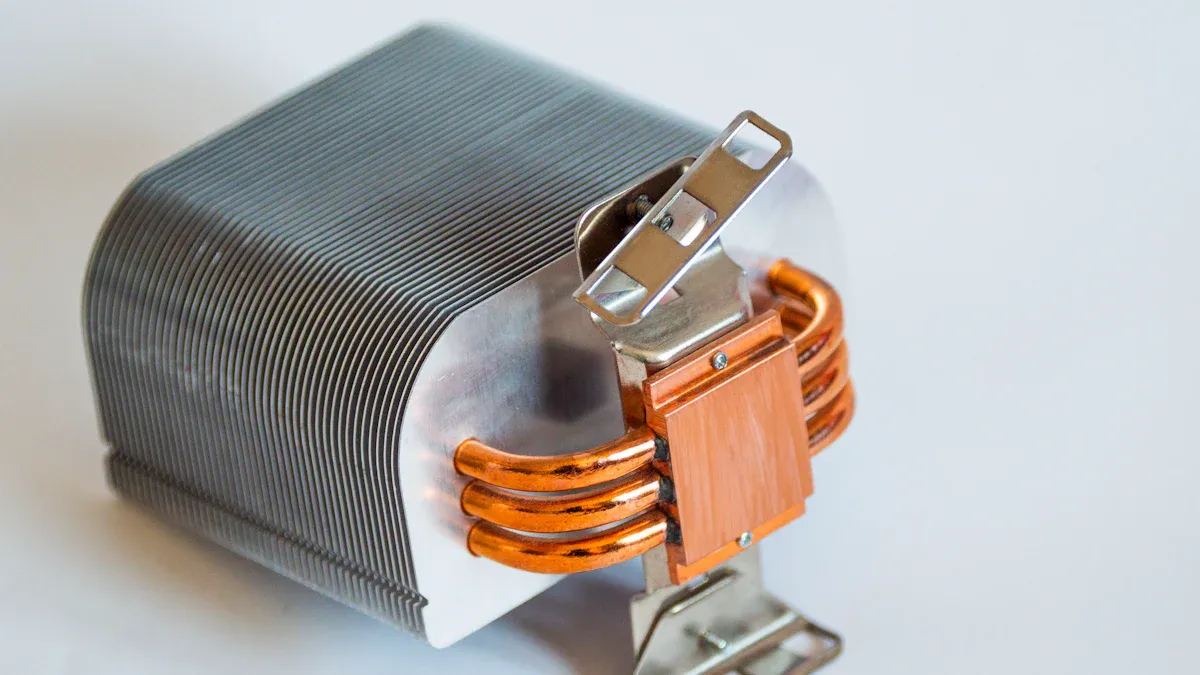
Definition and Core Function
A water cooling plate is also called a liquid cold plate. It helps keep devices cool when they get hot. You use it to move heat away from important parts like CPUs, GPUs, or batteries. The plate sits close to these parts. Coolant flows through the plate and takes the heat away. This keeps your electronics working well and stops them from getting too hot. Water cooling plates are used in big machines and in things people use every day. They are good at keeping temperatures steady.
Key Components
Plate Materials
You can pick from different materials for a water cooling plate. Each material changes how well the plate moves heat and how heavy it is. Here is a table that shows the most common choices:
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | ~205 | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, cost-effective |
| Copper | ~400 | Superior thermal conductivity, excellent temperature uniformity |
| Stainless Steel | N/A | Exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength |
Copper plates move heat the best. Aluminum plates are lighter and do not rust easily. Stainless steel plates are strong and last a long time.
Coolant Channels
Inside every water cooling plate, there are channels for the coolant. These channels touch the plate and go near the hot parts. The way the channels are made helps the coolant flow everywhere. This cools all areas and stops hot spots. The shape and size of the channels change how fast the coolant moves and how much heat the plate can take.
How Water Cooling Plates Work
Heat Transfer Process
When you use a water cooling plate, heat goes from the device into the plate. The plate takes in the heat by conduction. Copper and aluminum help because they let heat move fast. The coolant inside the channels picks up the heat and carries it away. This keeps things cool and protects your devices.
Tip: Plates with more surface area can take in more heat. Plates with lots of channels or fins work best for powerful devices.
Role of Coolant
The coolant is very important for the water cooling plate. You can use water, deionized water, or special fluids that do not carry electricity. The coolant moves through the channels, touches the hot parts, and takes the heat away. Then, the coolant goes to a heat exchanger or radiator and lets the heat out into the air. A pump keeps the coolant moving, so the plate stays cool and your devices are safe.
- You send the coolant to the hottest parts first.
- You stop hot spots by spreading the coolant everywhere.
- You change the flow speed to fit your cooling needs.
A water cooling plate helps get rid of heat and keeps things at the right temperature. Your electronics work better and last longer.
Main Functions and Operation
Heat Dissipation
A water cooling plate helps take heat away from hot parts. The plate sits close to things like processors or power modules. When your device is on, these parts get hot fast. The plate soaks up the heat and gives it to the coolant inside. The coolant moves the heat to a radiator or heat exchanger. There, the heat leaves and goes into the air.
A water cooling plate can remove more heat than air cooling. This lets your electronics work harder without getting too hot or slowing down.
Temperature Control
It is important to keep the temperature steady for electronics. If the temperature changes a lot, your device might not work or could break. The water cooling plate helps by spreading heat out and moving it away quickly.
Liquid cold plates use conduction and convection to move heat. The plate touches the hot part and pulls in the heat. The coolant picks up the heat and takes it away. Many plates use aluminum blocks with tubes or metal shells with fins. These designs help keep the temperature steady, even when your device works hard.
- Water is often better than other coolants. It keeps things cooler and more stable, which is good for devices that need careful control.
Efficiency Factors
Many things change how well your water cooling plate works. You want to move as much heat out as you can. Here are the main things that matter:
Flow Rate
How fast the coolant moves is very important. Faster coolant can take away more heat. You also need the right pressure so coolant goes everywhere. If the flow is slow, some parts may get hotter.
- Faster fluid helps the plate remove more heat.
- Good pressure makes sure coolant reaches every spot.
- Turbulent flow, where coolant mixes, can help move heat better.
Surface Area
The amount of plate touching the coolant matters a lot. More surface area means more places for heat to move into the coolant. Plates with lots of channels or fins give more area for the coolant to touch. This helps get rid of heat faster.
| Factor | How It Helps Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Channel Dimensions | Controls how fast and evenly coolant flows |
| Channel Orientation | Makes sure heat moves out quickly |
| Plate Material | Affects how fast heat moves into coolant |
| Surface Area | Gives more space for heat transfer |
Tip: If your device uses a lot of power, you need a plate that works really well. This lets your parts run at full speed without getting too hot.
Both flow rate and surface area are very important for cooling. Picking the right design keeps your electronics safe and working well.
Types of Water Cooling Plates
Standard Plates
Standard plates are used in many cooling systems. They have simple channels or tubes inside a metal block. The coolant moves through these channels and takes heat from the device. These plates work for most electronics and are easy to put in. You can find them in many shapes and sizes.
Here is a table that lists some common standard plates and how they are made:
| Type of Cooling Plate | Description |
|---|---|
| Stamped liquid cooling plates | Made by stamping metal, cost-effective for large numbers |
| Roll bond liquid cooling plates | Created by rolling metal sheets together, good for big projects |
| Extruded cooling plates | Made by pushing metal through a mold, allows for special shapes |
| Machining plus FSW plates | Combine cutting and friction stir welding for strong, custom plates |
| Copper tube cold plates | Use copper tubes inside a plate for fast heat transfer |
| Drilled liquid cold plates | Have holes and channels made by machines for smooth coolant flow |
Note: Standard plates are not too expensive and work well. You can use them in computers, power supplies, and other devices.
Microchannel Plates
Microchannel plates have lots of tiny channels inside. These small channels give more space for the coolant to touch. This helps the coolant take away more heat faster. Microchannel plates are good for things that get very hot in a small area.
- Microchannel plates move heat away very quickly.
- You can use them in powerful computers, power electronics, and medical devices.
- They are small and light, so you can use them in portable or flying electronics.
- Most flow rates are between 0.5 and 2.5 liters per minute. You do not need high pressure for good cooling.
- Microchannel plates can cool up to 50% better than standard plates.
Tip: If you need to cool something strong in a small space, microchannel plates are a good pick.
Custom Designs
Sometimes you need a water cooling plate made just for you. Custom designs let you choose the size, shape, and materials you want. You can ask for special channels, extra holes, or different shapes.
- Custom plates give the best heat transfer for your device.
- You can make them small to fit tight places.
- They last a long time if you take care of them.
- You get a plate made just for your needs.
Cooling Source can help you make custom plates for hard cooling problems. You can talk to experts to design a plate that fits your device and keeps it safe.
Material Options
When you pick a water cooling plate, you must think about the material. The right material helps your device stay cool and work well. Cooling Source gives you different choices, and each one has its own good points.
Copper Plates
Copper plates are great at moving heat away fast. They keep your electronics from getting too hot. You often find copper plates in powerful devices like CPUs and GPUs. These plates help your device run fast without overheating. Copper spreads heat out, so you do not get hot spots. If you want the best cooling, copper plates are a smart pick.
Tip: Copper plates are best for devices that need strong and steady cooling.
Aluminum Plates
Aluminum plates are light and do not cost much. Aluminum moves heat away quickly, so it keeps your device cool. You can use aluminum plates in many electronics, like computers and power supplies. These plates do not rust easily, so they last a long time. Aluminum plates weigh less than copper, so they are easier to use. If you want good cooling and want to save money, aluminum plates are a great choice.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Weight | Cost | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | ~400 | Heavier | Higher | Moderate |
| Aluminum | ~205 | Lighter | Lower | High |
Note: If you mix copper and aluminum, you can get galvanic corrosion. This can make your cooling plate not work as well or not last as long. Always check your setup before you use both materials together.
Dielectric Fluids
Dielectric fluids help keep your electronics safe. These fluids do not carry electricity, so they stop short circuits. You can use dielectric fluids in water cooling plates for medical gear, electric cars, and other high-tech things. These fluids keep your device cool and safe, even when you need strong cooling. Cooling Source has different fluids, so you can pick what works best for you.
- Dielectric fluids stop electrical problems.
- You can use them where water might hurt your device.
- These fluids work well with copper and aluminum plates.
Picking the right material for your water cooling plate helps your device stay cool and last longer. You can talk to Cooling Source experts to find the best match for your needs.
Applications and Benefits

Electronics Cooling
Water cooling plates help keep electronics safe and working well. They are used in many places where heat can be a problem. Data centers use them to cool servers and keep things running. Telecommunications equipment stays reliable with steady cooling. Aerospace and defense systems use them to protect important electronics. Power electronics, computers, and server towers all need good heat control. You also find water cooling plates in cars, wind turbines, lasers, and electric aircraft.
CPUs and GPUs
When you play games or do hard work on a computer, the CPU and GPU get hot. A water cooling plate helps keep them cool. It keeps the temperature low, even when you use your computer a lot. This lets your graphics card work its best without slowing down. You also hear less noise because you do not need as many fans. Liquid cooling lets your computer do big jobs without getting too hot. Cold plates can handle very high heat, even up to kilowatt levels. You can use them in warm-water loops, which helps reuse heat in some setups. They fit new hardware easily, so you do not have to change your system.
Tip: If you want your computer to be quiet and fast, use a water cooling plate.
High-Power Devices
High-power devices in factories or power plants make a lot of heat. You need strong cooling to keep them safe. Water cooling plates move heat away fast, so your equipment lasts longer and works better. You see these plates in power converters, industrial lasers, and big battery packs.
Medical Equipment
MRI and Lasers
Medical machines like MRI scanners and surgical lasers need steady temperatures. Water cooling plates help by moving heat away from sensitive parts. This keeps the machines safe and ready to use. They give stable cooling, so the equipment does not overheat. MRI machines and lasers use them to handle strong heat during scans or treatments. Their small size makes medical devices lighter and easier to move. They work quietly, which helps patients and staff stay calm. You get good temperature control, so the machines always work their best.
Note: Hospitals and clinics trust water cooling plates to keep important machines safe.
Electric Vehicles
Battery Management
Electric vehicles need good cooling for their batteries. A water cooling plate helps control battery temperature by moving coolant through special channels. This keeps the battery from getting too hot or too cold.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | High-thermal-conductivity aluminum |
| Cooling Method | Uses a two-phase coolant, better than air cooling |
| Heat Dissipation | Removes heat from each cell, boosts charging and discharging performance |
| Battery Life Extension | Keeps batteries at the right temperature, so they last longer |
The cooling plate moves heat away during charging and driving. It keeps the battery at the best temperature for top performance. It helps the battery last longer by stopping overheating. In cold weather, it can even help warm the battery for better use. You see water cooling plates in electric cars, buses, and new electric planes. They help your vehicle run safely and work well.
Key Advantages
If you pick a water cooling plate, your devices get many good things. These benefits help your electronics work well, last longer, and stay safe when used a lot.
Performance
You want your electronics to work their best. A water cooling plate helps move heat away fast, especially from strong parts. The liquid inside the plate takes heat out much quicker than air. This means your device can do more work without getting too hot.
- Liquid cooling systems are smaller. You can use them in tight spaces.
- They save energy. The system uses less power to cool your device, so your bills go down and you help the planet.
- Liquid moves heat up to four times better than air. This lets your electronics go faster and work better, even in small places.
Tip: If you want your computer or device to work its hardest, liquid cooling helps you get the most from your hardware.
Reliability
Keeping your electronics cool makes them work better for longer. Using a water cooling plate stops your device from getting too hot. This helps stop sudden shutdowns or damage.
- Liquid cooling systems take away extra heat better than air-cooled heat sinks, especially in powerful devices.
- The liquid inside holds more heat and moves it faster than air. This is great for strong electronics.
- You can change things like temperature and flow speed to fit what you need.
- Liquid cold plates are small, so you can make your system compact and reliable.
Note: Many people who use modern PCs like liquid cooling because it keeps their computers steady and safe.
Longevity
You want your electronics to last a long time. Good cooling helps you reach this goal. A water cooling plate keeps the temperature steady, so your parts do not wear out fast.
- Better cooling means your parts do not get too hot, so they last longer.
- The system stops thermal stress, which can break parts over time.
- With better cooling, you can even run your device faster for longer.
Remember: Keeping your electronics cool helps them work well and last longer.
Picking a water cooling plate gives you strong performance, steady work, and longer life for your devices. You can feel good knowing your electronics are safe with advanced cooling.
Choosing the Right Water Cooling Plate
Compatibility
When you choose a water cooling plate, you need to make sure it fits your device and works with your system. Compatibility matters because the right fit helps your cooling system work better and last longer.
Device Size and Shape
You should check the size and shape of your device before picking a cooling plate. The plate must cover the parts that get hot. If the plate is too small, it will not cool everything. If it is too big, it may not fit in your device. You also want to think about the weight. Lighter plates work better in things like drones or airplanes. Heavy plates can slow down or unbalance your device.
Coolant Type
The type of coolant you use is important. Some plates work best with water, while others need special fluids that do not carry electricity. You must make sure the coolant does not react with the plate material. For example, mixing the wrong coolant with aluminum or copper can cause damage over time. Always check what your device needs and what the plate can handle.
Here is a table to help you see what to consider when checking compatibility:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Performance | Check if the plate can handle the heat your device makes. |
| Manufacturing Cost | Pick a plate that fits your budget and cooling needs. |
| Size and Weight | Make sure the plate fits your device and is not too heavy. |
| Installation and Maintenance | Choose a design that is easy to install and keep clean. |
| Fluid Compatibility | Use a coolant that works well with the plate material. |
| Operational Environment | Think about where you use your device—temperature, humidity, and possible exposure to chemicals. |
| Scalability and Future-Proofing | Pick a plate that can work with upgrades or changes in your system later. |
Performance Needs
You need to know how much heat your device makes. Devices that work hard or run for a long time need more cooling. The design of the water cooling plate changes how well it moves heat away. Some plates have low resistance and let coolant flow fast. Others slow the coolant down to pick up more heat. You should look at how the plate handles pressure and flow. The pump and coolant path also affect how well the plate works. If you want your device to stay cool, match the plate’s performance to your needs.
Tip: Always check the heat output of your device. Pick a plate that can handle more heat than you expect, so your device stays safe.
Cost Considerations
You want good cooling, but you also want to save money. The price of a cooling plate depends on its size, shape, and how it is made. Simple stamped plates often cost less, sometimes around $60 for medium or small sizes. If you need a special shape or lots of channels, the price can go up. Making a new mold for a custom plate costs more at first, but it can save money if you need many plates. Always balance your budget with your cooling needs.
Note: Think about both the first cost and how much you will spend to keep the plate working over time.
Customization Options
Sometimes your device needs a water cooling plate that fits perfectly. Not every plate works for every project. Customization helps you get what you need. You can pick the size, shape, and material of your plate. You can also choose how the coolant moves inside.
There are different ways to make custom plates. Each way has its own benefits:
- Friction Stir Welded (FSW) Cold Plates use a special welding method. They are strong and do not leak. These plates work well in high-pressure systems.
- Vacuum Brazed Cold Plates join metal parts without melting them. They are seamless and do not leak. You can use them for complex shapes.
- Tube Embedded Heat Sinks have tubes inside the plate. They cost less and work for devices that do not need a lot of cooling.
- Die Cast Liquid Cold Plates are made by pouring metal into a mold. They are light and easy to shape. These plates are good for electronics people use every day.
- Extruded Liquid Cooling Heat Sinks are made by pushing metal through a shaped hole. They are tough and work well in factories.
- Gun Drilled Liquid Cold Plates have deep, straight holes for coolant. They are best for long and exact cooling paths.
Here is a table to help you compare these choices:
| Type of Cold Plate | Description |
|---|---|
| Friction Stir Welded (FSW) Cold Plates | Good for high-pressure jobs and strong builds. |
| Vacuum Brazed Cold Plates | Seamless and leak-proof for tricky designs. |
| Tube Embedded Heat Sinks | Cheap and flexible for medium cooling needs. |
| Die Cast Liquid Cold Plates | Light and easy to change, great for home electronics. |
| Extruded Liquid Cooling Heat Sinks | Strong and efficient, best for big machines. |
| Gun Drilled Liquid Cold Plates | Great for jobs needing exact coolant paths. |
When you make your own water cooling plate, you can add features to help your device:
- Enhanced Heat Transfer means special channels move heat away faster.
- Compact Design lets the plate fit in small spaces. You do not need big fans or extra parts.
- Longevity means the plate protects your device and helps it last longer.
Tip: If you have a special device or project, ask Cooling Source experts for help. They can help you design a water cooling plate that fits and keeps your equipment safe.
Customizing your water cooling plate gives you more control. Your device stays cool, works better, and lasts longer. You can feel sure your electronics are protected.
Installation and Maintenance
Installing and maintaining your water cooling plate helps your device stay cool and last longer. You can follow these steps to set up your system and keep it running smoothly.
Installation Steps
Preparation
You need to get ready before you start. First, check if your device and case have enough space for the water cooling plate. Make sure the plate fits your CPU socket or the part you want to cool. Gather all the tools you need, like a Phillips screwdriver and thermal paste. Lay out your cooling plate, mounting brackets, and any screws or fittings.
Mounting
Start by preparing the cooler. If your plate needs thermal paste, apply a small amount to the surface that will touch the hot part. Attach the mounting brackets to your device. Next, choose a spot for the radiator or heat exchanger. Secure it in place with screws. Make sure the radiator has good airflow around it.
Now, align the cooling plate over the part you want to cool, such as the CPU or battery. Gently press it down and fasten it with the provided screws. Check that the plate sits flat and covers the whole area.
Coolant Connection
Connect the coolant tubes to the inlet and outlet ports on the plate. Tighten the fittings so they do not leak. Fill the system with your chosen coolant, such as water, deionized water, or a dielectric fluid. Use a pump to move the coolant through the system. Watch for leaks as you fill and run the system for the first time.
Tip: Always double-check all connections before turning on your device. This helps prevent leaks and keeps your electronics safe.
Maintenance Tips
You need to take care of your water cooling plate to keep it working well. Regular maintenance stops problems before they start.
Cleaning
Keep your cooling plate and system clean. Dust and dirt can block airflow and slow down heat transfer. Wipe down the outside of the plate and radiator. Flush the coolant system every few months to remove any buildup or biological growth.
Leak Prevention
Check all fittings and tubes for signs of leaks. Tighten any loose connections. Replace worn-out seals or hoses right away. Using the right coolant helps prevent corrosion and scaling inside the plate.
Inspections
Inspect your system often. Look for wear, blockages, or changes in coolant color. Monitor the temperature and flow rate. If you see higher temperatures or slower flow, clean or replace parts as needed. Set a schedule for regular checks and coolant changes.
Note: Good maintenance keeps your water cooling plate efficient and extends the life of your electronics.
Water Cooling Plate vs. Other Cooling Methods
Air Cooling Comparison
You might wonder how water cooling plates compare to air cooling. Air cooling uses fans to blow air over heat sinks or parts. This works for many devices, but it cannot remove as much heat. Water cooling plates use liquid to take heat away. This makes them much better at cooling.
Look at this table to see how well each method works:
| Cooling System | Fan Speed (rpm) | Cooling Efficiency Increase (%) | Inlet Flow Rate (m/s) | Cooling Efficiency Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air-Cooled Motor | 800 to 2000 | 27.78 | N/A | N/A |
| Water-Cooled Motor | N/A | N/A | 0.1 to 0.9 | 67.47 |
Water cooling plates can cool more than twice as well as air cooling. This means your device stays cooler, even when it works hard.
Tip: If you need to cool strong electronics or want less noise, water cooling plates are a great choice over air cooling.
Heat Sink Comparison
Heat sinks are another way to cool electronics. They have metal fins that spread heat into the air. This works for devices that do not get very hot. Water cooling plates use liquid to move heat away faster and more evenly.
Here is a table that shows the main differences:
| Feature | Heat Sink | Cold Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Mechanism | Air cooling using fins | Liquid cooling with coolant |
| Design Complexity | Simpler design with fins | More complex with internal channels |
| Thermal Performance | Adequate for lower-power apps | Superior for high-power applications |
| Manufacturing | Easier to manufacture | Requires advanced techniques |
- Heat sinks use air, but cold plates use liquid.
- Cold plates cool high-power devices better.
- Heat sinks are simple, but cold plates are harder to make.
Note: If your device gets very hot or needs steady temperatures, a water cooling plate works better than a heat sink.
When to Choose Water Cooling Plates
Pick a water cooling plate when your device needs strong and steady cooling. Here are some times when this method is best:
| Scenario Type | Description |
|---|---|
| High heat load environments | Cold plates are best for lots of heat. |
| Limited space applications | Good when you do not have much room. |
| High-performance computing | Needed for sensitive electronics that need good cooling. |
| Precise temperature control | Great for things that need exact temperatures. |
If you use powerful computers, medical machines, or electric cars, water cooling plates help keep things cool. You also get more ways to design your system, which helps in small spaces or when you need steady temperatures.
Remember: If your project needs the best cooling, a water cooling plate is often the right pick.
You have learned that a water cooling plate uses liquid channels to take heat away from your device. This helps keep electronics cool and safe. Cooling Source has options for computers, cars, and medical machines. Before picking one, check these key things:
| Factor | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Performance | Handles lots of heat from strong parts |
| Compatibility | Fits your device and works with your hardware |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and lasts a long time |
| Customization | Can be made to fit your needs and space |
Think about what you need, how much money you want to spend, and how much room you have. Custom plates and good care help your system last longer and work better.
FAQ
What is the main benefit of using a water cooling plate?
You get better cooling for your electronics. Water cooling plates move heat away faster than air. This helps your devices work harder and last longer.
Can I use regular tap water as coolant?
You should not use tap water. Tap water can cause corrosion or buildup inside the plate. Use deionized water or a special coolant for the best results.
How often should I check or maintain my water cooling plate?
Check your system every three months. Look for leaks, clean dust, and replace coolant if it looks dirty. Regular checks help your cooling plate work well.
Are water cooling plates safe for home computers?
Yes, water cooling plates are safe for home computers. You must install them correctly and check for leaks. Many people use them to keep gaming PCs cool and quiet.
What materials work best for water cooling plates?
Copper and aluminum work best. Copper moves heat very well. Aluminum is lighter and costs less. Both materials help keep your devices cool.
Can I customize a water cooling plate for my project?
Yes, you can. Companies like Cooling Source offer custom sizes, shapes, and materials. Custom plates fit your device and give you the best cooling.
Do water cooling plates make noise?
Water cooling plates make very little noise. Pumps and fans in the system may make a soft sound. You will notice less noise than with air cooling.




