Extrusion heat sink vs cold forging heat sink

Comparing Cooling Solutions for Electronics
Explore the differences between extrusion and cold forging heat sinks.
| Features | Extruded Heat Sink | Forged Heat Sink |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-quality extruded aluminum | Advanced cold forged aluminum |
| Cooling Efficiency | Good thermal performance | Cools up to 14% better |
| Shape Complexity | Limited to simple shapes | Allows complex shapes |
| Production Speed | 20-30 units/hour | 10-15 units/hour |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront investment | Higher initial cost |
| Durability | Good reliability | Stronger and more durable |
| Customization Options | Highly customizable | Limited customization |
| Material Waste | 3%-5% waste | 8%-12% waste |
| Application Suitability | Versatile for many electronics | Ideal for high-performance systems |
You want your devices to stay cool. Picking between Tran-Tec’s extruded heat sinks and Radian’s cold forging depends on what you need. Extruded heat sinks usually cost less. They work well for most electronics. Cold forging, like Radian’s, cools up to 14% better. It also lets you make more complex shapes. Look at the cost comparison below:
| Cost Factor | Extrusion | Cold Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Investment | $400,000-$800,000 | $150,000-$300,000 |
| Labor Costs per Unit | $15-$25 | $25-$40 |
| Material Efficiency | 3%-5% waste | 8%-12% waste |
| Production Speed | 20-30 units/hour | 10-15 units/hour |
Think about your money, how well you want it to work, and how many you need before you pick a heat sink.
Key Takeaways
- Extruded heat sinks cost less and work for most electronics. They are a good pick for big orders. Cold forged heat sinks cool better by up to 14%. They are best for powerful devices and important systems. Think about how many you need to make. Extrusion works well for lots of units. Cold forging is better for small, special batches. Customization is different for each type. Extrusion lets you change designs more easily. Cold forging cannot change as much but can make complex shapes. Look at your budget before choosing. Extrusion costs less at first. Cold forging can save money later because it uses materials better. Extrusion is faster for making samples and products. It can make up to 30 units each hour. Cold forging makes about 15 units per hour. Pick extrusion for normal electronics and saving money. Pick cold forging if you need better performance and strength. Always choose the right heat sink for your cooling needs, budget, and how many you need.
Heat Sink Overview

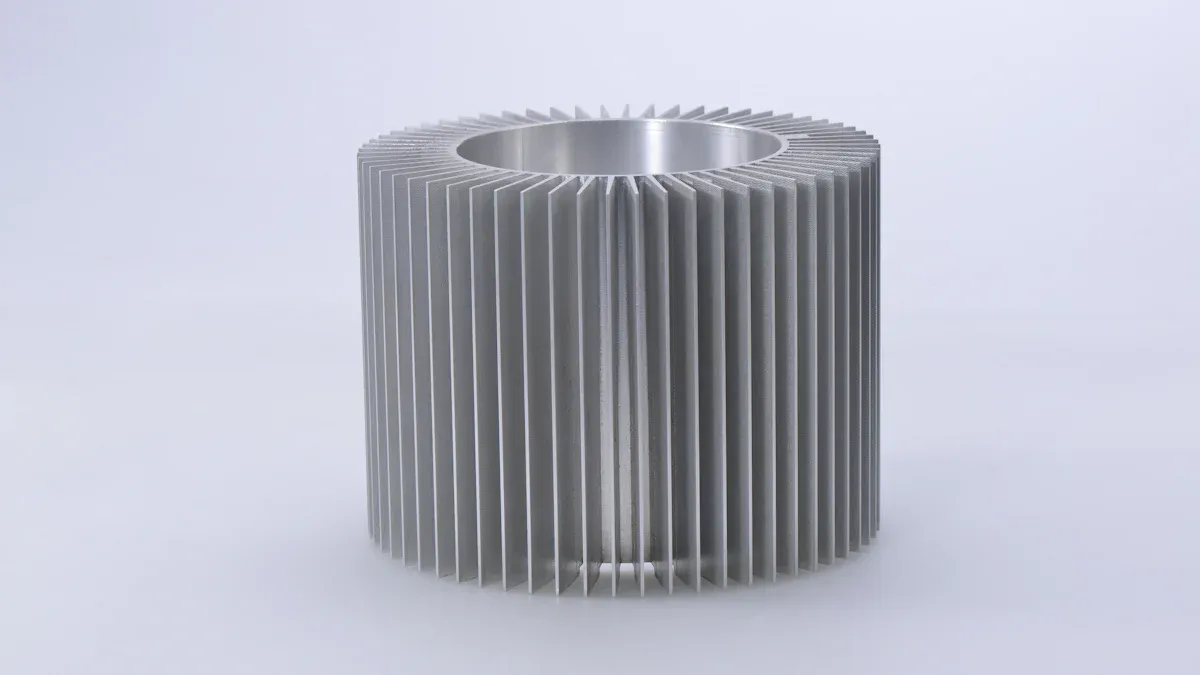
Extrusion
Extruded heat sinks are used in many electronics. Tran-Tec offers lots of choices for these. The extrusion process pushes hot aluminum through a shaped mold. This makes long pieces with the same shape all the way through. You can cut and shape these pieces to fit what you need. Extruded heat sinks are good for most cooling jobs. They give you a good mix of price and how well they work.
You might pick an extruded heat sink because it is flexible. Tran-Tec has many shapes and sizes to choose from. You can ask for special changes if you need them. This helps you match the heat sink to your project. People use extruded heat sinks for things like:
- Automotive: Cooling electronics in electric and hybrid cars.
- Industrial equipment: Keeping motors and power supplies cool.
- Renewable energy: Managing heat in solar and wind power devices.
- Consumer electronics: Stopping game consoles and audio gear from getting too hot.
Extruded heat sinks help cool many devices you use every day. They are affordable and work for most needs.
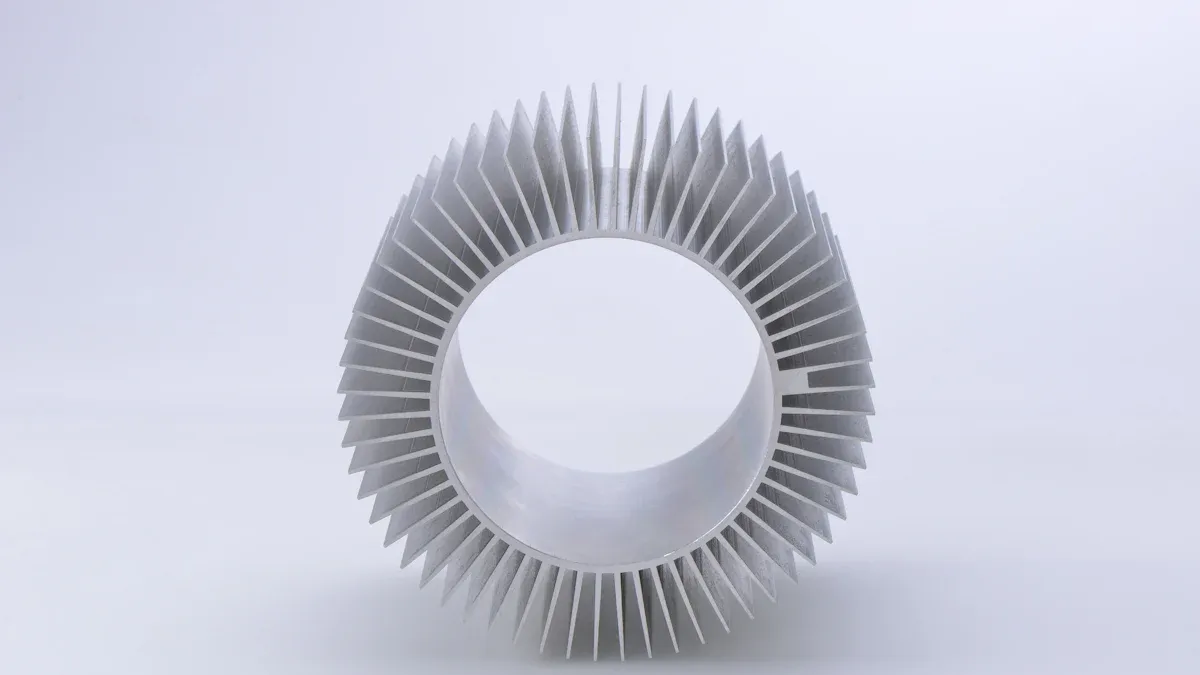
Cold Forging
Cold forging makes heat sinks in a different way. Radian is known for its forged heat sinks. The process uses strong pressure to shape metal without heating it. This packs the metal tightly, so the heat sink is solid and tough. Cold forging lets you make more detailed shapes, like round pins or oval fins.
You might choose a cold forging heat sink for better cooling. Radian’s heat sinks can cool up to 14% more than regular extrusions. You can also add copper parts to move heat even faster. Cold forging is great for advanced electronics and powerful systems.
Cold forged heat sinks are found in:
- Computers and servers: Cooling CPUs and GPUs when working hard.
- LED lighting: Keeping LEDs cool so they last longer.
- Automotive electronics: Making sure engine controls and power modules work well.
- Industrial electronics: Handling tough jobs in power and control systems.
Cold forging gives you a heat sink for hard tasks. You get stronger cooling and more ways to design it for special projects.
Comparison Table
Key Metrics
When you compare extrusion and cold forging, you see big differences in cost, speed, and how well each method works. You want to know which heat sink fits your project best. The table below shows the main points side by side:
| Factor | Extrusion Heatsink | Cold Forged Heatsink | Best Use | Savings Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Cost ($) | 2-5 | 15-20 | Mass vs. Niche | 60% vs. 0% |
| Lead Time (weeks) | 2-3 | 4-6 | Fast vs. Planned | 1-2 vs. 0 |
| ROI (5 years, %) | 150 | 200 | Budget vs. Premium | Low vs. High |
| Production Volume | 10,000 | 2,000 | Scalable vs. Limited | High vs. Low |
| Failure Rate (%) | 2 | 0.5 | General vs. Critical | Acceptable vs. Tight |
You see that extrusion heatsinks cost less and arrive faster. You can order large batches for big projects. Cold forged heatsinks cost more, but you get better cooling and lower failure rates. These work best for high-performance electronics or critical systems.
Tip: If you need thousands of units quickly and want to save money, extrusion is the way to go. If you need top cooling and reliability, cold forging is your best choice.
Look at the chart below. It shows how extrusion and cold forging compare for cost, lead time, ROI, production volume, and failure rate.
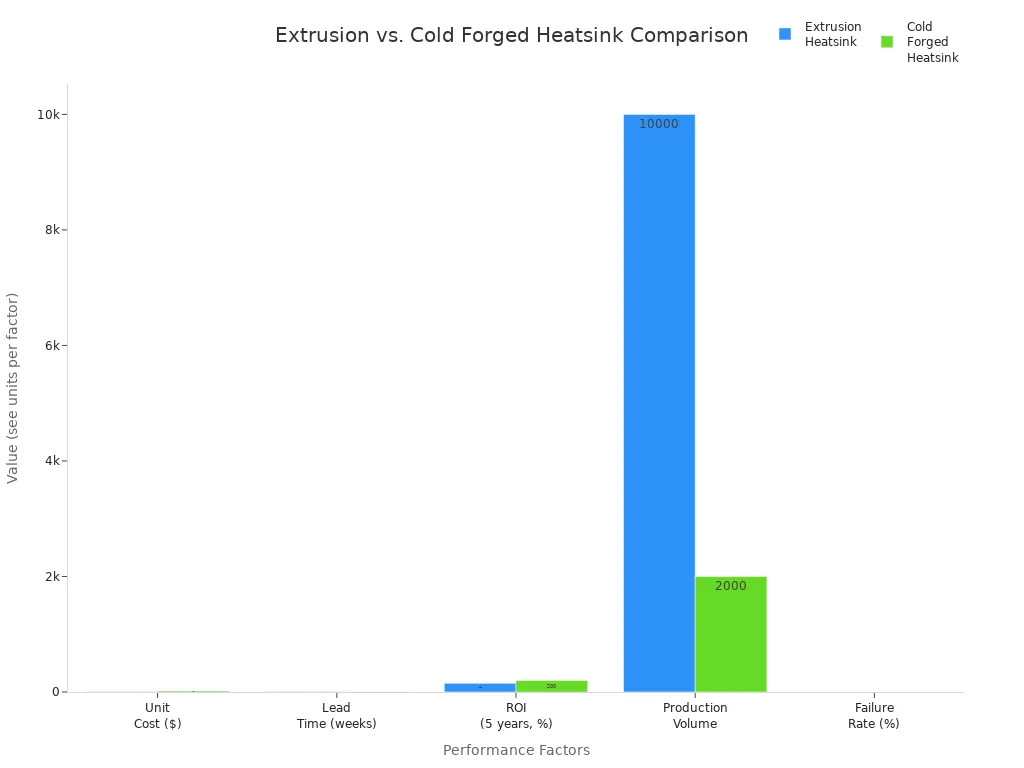
You can see that extrusion heatsinks give you savings and speed. Cold forged heatsinks give you better performance and reliability. You should match your choice to your needs. If you want a heat sink for everyday electronics, extrusion works well. If you build high-power devices, cold forging gives you the edge.
Manufacturing Process

Extrusion Steps
To make an extruded heat sink, you start with a solid aluminum billet. Tran-Tec pushes this billet through a shaped die using high pressure. The metal comes out as a long piece with the same shape as the die. Workers cut these pieces to the size you need. They can also machine the heat sink to add holes or slots. You can ask for changes like shorter fins or more mounting space. This process is good for making many heat sinks quickly. You get lots of choices in shape and size. It is easy to change an old design to fit new needs.
Cold Forging Steps
Cold forging works differently. Radian uses a metal slug, usually aluminum. They do not heat the metal. Instead, they use a strong press to push it into a die at room temperature. This packs the metal tightly and makes it very dense. The process can make complex shapes like round pins or oval fins. These shapes help move heat away faster. After forging, workers may machine the heat sink for small details or add copper inserts. Cold forging makes strong and detailed parts. But you cannot change shapes easily without making a new die.
Material Options
You can pick from different materials. Each one changes how well your heat sink works. Here are some important things to know:
- Cold forging lines up the metal atoms. This lowers thermal resistance and helps heat move out faster.
- The process lets you make detailed fin designs. You get more surface area to cool your device.
- Cold forging makes a dense and even structure. This means fewer air gaps and better heat transfer.
- Cold forging may cost more at first. But it can save money later because you waste less material and make better parts.
When you look at customization and scalability, you see big differences. The table below shows how each method compares:
| Feature | Cold Forging | Extrusion (Tran-Tec) |
|---|---|---|
| Customization | Limited to specific shapes and sizes | High versatility in shapes and sizes |
| Scalability | Lower production volume | High production volume capabilities |
| Material Choice | Mainly aluminum | Wide range including copper alloys |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Cost-effective long-term | Cost-effective for large batches |
Note: If you want a special shape or need thousands of heat sinks, extrusion gives you more choices and faster results. If you need the best cooling and can use standard shapes, cold forging gives you top performance.
Heat Sink Performance
Thermal Conductivity
You want your devices to stay cool, so you need to know how well each type of heat sink moves heat away from your components. Cold forging gives you a clear advantage here. The process packs the metal tightly, which means heat travels through it faster. Radian’s cold forged heat sinks can cool up to 14% better than extruded ones. This difference matters most when you work with high-power electronics or need to keep temperatures as low as possible.
Extruded heat sinks, like those from Tran-Tec, still offer good thermal conductivity. The aluminum used in extrusion works well for most electronics. If you do not need the absolute best cooling, extrusion gives you reliable performance at a lower cost.
Tip: If your project needs the best cooling, cold forging is the top choice. For everyday electronics, extrusion usually does the job.
Surface Area
The amount of surface area on a heat sink affects how much heat it can release into the air. Cold forging lets you create complex shapes, such as round pins or tall, thin fins. These designs give you more surface area in the same space. More surface area means better cooling.
Tran-Tec’s extruded heat sinks have straight fins and standard shapes. You can pick from many sizes, but the shapes are simpler. This works well for most uses, but you might not get as much surface area as with cold forging.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Feature | Extrusion (Tran-Tec) | Cold Forging (Radian) |
|---|---|---|
| Fin Shape | Straight, uniform | Pins, elliptical, tall |
| Max Aspect Ratio | 10:1 | Up to 35:1 |
| Surface Area | Standard | High |
You should choose cold forging if you need the most surface area in a small space. For standard projects, extrusion gives you enough cooling.
Durability
Durability means your heat sink will last and keep working under stress. Cold forged heat sinks have a dense, strong structure. The forging process makes them tough and less likely to crack or break. You can use them in harsh environments, like cars or industrial machines, and trust they will hold up.
Extruded heat sinks are also strong. Tran-Tec uses high-quality aluminum, so you get good reliability. For most electronics, extrusion gives you enough strength and a long life.
Note: If you need a heat sink for a tough job or a place with lots of vibration, cold forging gives you extra peace of mind. For regular electronics, extrusion offers solid durability.
In real-world use, both types perform well. Cold forging stands out when you need the best cooling and the strongest structure. Extrusion works for most everyday needs and gives you a good balance of performance and cost.
Cost and ROI
Initial Cost
When you start a new project, you want to know how much money you need upfront. Extrusion usually costs less at the beginning. You pay for the aluminum and the extrusion die, which is simple and affordable. This makes extrusion a good choice if you want to test ideas or launch a small batch. Cold forging needs more investment at the start. You pay for stronger presses and more complex dies. The process uses more force, so the equipment costs more. If you plan to make only a few heat sinks, extrusion helps you save money.
Tooling
Tooling plays a big role in your budget. You need dies and machines to shape the metal. Here is how tooling costs compare:
- Extrusion tooling costs less. You can make simple shapes without spending much.
- Cold forging tooling costs more. The dies are stronger and more detailed, which raises the price.
- If you want to change the design, extrusion lets you adjust the die or machine the part easily.
- Cold forging needs a new die for each major change, which adds to the cost.
You should think about how often you want to change your design. If you need flexibility, extrusion gives you more options for less money.
Volume Impact
Production volume changes your cost over time. If you make thousands of heat sinks, extrusion gives you big savings. The process runs fast and uses less material. You can scale up easily and keep costs low. Cold forging works best for large batches. The higher tooling cost pays off when you make many units. The process becomes more efficient, and you waste less material. You get better performance, which can save money in the long run.
Here is a table to help you compare:
| Production Volume | Extrusion Cost per Unit | Cold Forging Cost per Unit | Best Choice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (100-500) | Low | High | Extrusion |
| Medium (1,000-5,000) | Moderate | Moderate | Both |
| High (10,000+) | Lowest | Lowest | Cold Forging |
Tip: If you want to launch a new product or test a design, extrusion helps you start small. If you plan to make many units and need top performance, cold forging gives you better value over time.
You should match your choice to your project size and goals. Think about how many units you need and how much you want to spend now and later. The right heat sink helps you save money and get the best results.
Lead Time and Flexibility
Prototyping
You want to try your ideas before making a lot. Tran-Tec helps you test with their sample program. You can get a few extruded heat sinks to see if they fit and cool well. This helps you find problems early and saves money. Extrusion lets you get prototypes fast. Making the tooling takes about 7 days. You can get your prototype in about 15 days. Radian also helps with prototyping, especially for cold forging. Their process can make a cold forged heat sink in just 8 days. Fast prototyping lets you test designs quickly.
Quick testing helps you fix mistakes early and make your design better before making many heat sinks.
Production
Production speed is important when you need lots of heat sinks. Extrusion is fast after the tooling is ready. It takes about 21 days to finish production. You can make 20-30 heat sinks each hour with extrusion. Cold forging is a little slower. The lead time for cold forging is about 20 days. You can make 10-15 heat sinks each hour with cold forging. If you need thousands fast, extrusion is better. Cold forging is good for small batches or special shapes.
Here is a table that shows lead times:
| Process Type | Lead Time (Days) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Extrusion Heat Sink | 15 |
| Cold Forging Heat Sink | 20 |
If you want lots of heat sinks fast, choose extrusion. If you want special shapes, cold forging is a good choice.
Customization
Customization helps you match the heat sink to your project. Tran-Tec gives you many choices. You can pick bonded fin, folded fin, machined fin, or liquid cooled heat sinks. You can ask for shorter fins or more mounting space. This makes it easy to get the right heat sink for your device. Radian’s cold forging lets you make cool shapes, like round pins or oval fins, in one step. Cold forging can add copper parts for better cooling. You can change the height using the same die, which saves time and money.
| Customization Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Bonded Fin Heat Sinks | Baseplate with metal fins, glued with epoxy. |
| Folded Fin Heat Sinks | Thin metal folded and attached with glue or solder. |
| Machined Fin Heat Sinks | Cut from solid blocks for testing. |
| Liquid Cooled Heat Sinks | Plate with channels for cooling fluid, can be changed for different uses. |
Extrusion gives you more choices if you want to change designs often. Cold forging is best for strong heat sinks and special shapes.
Application Suitability
Electronics
You want your electronics to stay cool and last longer. Tran-Tec’s extruded heat sinks work for most home devices. You can find them in game consoles and audio gear. They are also used in RF radar systems. Tran-Tec makes parts for RF radar, like ferrite circulators and ceramic bandpass filters. These need good cooling to work well. Extrusion gives you a good mix of price and performance.
Radian’s cold forging heat sinks are for advanced electronics. You see them in computers, servers, and LED lights. These heat sinks have special shapes to move heat away fast. If your device gets very hot or needs to be super reliable, cold forging cools better.
Tip: Use extrusion for everyday electronics and big orders. Pick cold forging for high-end devices or when you need the best cooling.
Automotive
Cars need strong and steady cooling. Extruded heat sinks are used in electric and hybrid cars. Tran-Tec’s products help cool power modules and control units. These heat sinks can handle shaking and changing temperatures.
Cold forging is best for important car electronics. Radian’s forged heat sinks are extra strong and last longer. You find them in engine controls and high-power modules. Their solid build stops cracks and keeps your car safe.
| Application Area | Extrusion (Tran-Tec) | Cold Forging (Radian) |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicles | Power modules, control units | Engine controls, high-power |
| Hybrid Cars | Battery cooling, sensors | Power electronics, safety |
Note: Use extrusion for regular car electronics. Use cold forging for tough jobs or when you need top safety.
High Power
High-power machines need the best cooling. Radian’s cold forging heat sinks are used in big machines and powerful electronics. They use tall fins and copper parts to move heat fast. These heat sinks are for jobs where too much heat can break things.
Tran-Tec’s extruded heat sinks also work in high-power places. You see them in solar panels and factory machines. They cool well and cost less. If you need to cool lots of units, extrusion saves money.
- Tran-Tec: Used in solar panels, wind turbines, and big motors.
- Radian: Used in high-power control systems, safety gear, and flame-resistant equipment.
Tip: For the hardest jobs and most power, cold forging is best. For big projects with many pieces, extrusion saves money and works well.
Pros and Cons
Extrusion
When you look at extrusion heat sinks, you find many reasons to choose them for your project. You get fast production, lower costs, and a wide range of shapes. Tran-Tec’s extruded heat sinks work well for most electronics. You can order large batches and get them quickly. If you want to change the design, you can do it without much trouble.
Pros of Extrusion Heat Sinks:
- High production speed: You can get up to 500 units per hour. This helps when you need many heat sinks fast.
- Cost-effective: You save money, especially if you need a lot of units. The process uses less energy and simple tools.
- Versatile applications: You can use these heat sinks in many devices, from computers to cars.
- Easy customization: You can ask for different shapes, sizes, or extra features. Tran-Tec can adjust the design to fit your needs.
- Lightweight: The aluminum used in extrusion keeps your device light.
Cons of Extrusion Heat Sinks:
- Thermal performance: You get good cooling, but not the best. If your device gets very hot, you may need more.
- Shape limits: The process makes straight fins and simple shapes. You cannot get very complex designs.
- Material density: The metal is not as dense as cold forged heat sinks, so it may not handle extreme heat as well.
If you want a heat sink that is affordable, quick to make, and fits many uses, extrusion is a smart choice.
Cold Forging
Cold forging heat sinks, like those from Radian, give you top cooling and strong parts. You get a dense, solid heat sink that moves heat away fast. The process lets you create detailed shapes, such as round pins or tall fins, which boost cooling.
Pros of Cold Forging Heat Sinks:
- Excellent thermal conductivity: The dense structure moves heat quickly. Your device stays cooler, even under heavy use.
- Strong and durable: Cold forging makes the metal tough. You can use these heat sinks in harsh places.
- Complex shapes: You can design pins, ovals, or tall fins. This gives you more surface area for better cooling.
- Ideal for high-performance: These heat sinks work best in powerful electronics or critical systems.
Cons of Cold Forging Heat Sinks:
- Higher cost: You pay more for each unit. The process uses more force and detailed dies.
- Slower production: You get about 200 units per hour. This is slower than extrusion.
- Less flexible for changes: If you want a new shape, you need a new die. This takes time and money.
| Feature | Extrusion Heat Sinks | Cold Forging Heat Sinks |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | High (500 units/hour) | Moderate (200 units/hour) |
| Cost | Cost-effective for high-volume production | Higher cost due to precision |
| Thermal Performance | Good thermal performance, lightweight | Excellent thermal conductivity, dense and strong |
| Application Suitability | Versatile, suitable for electronics | Ideal for high-performance applications |
Choose cold forging if you need the best cooling and strength, even if it costs more and takes longer to make.
Decision Factors
Quick Guide
When you pick between extrusion and cold forging heat sinks, you should think about a few main things. Each way works best for different jobs. You want to choose what fits your project.
Material Characteristics
You need to see how your metal handles heat and pressure. Aluminum is good for both extrusion and cold forging. Magnesium is light and easy to shape, so it works well for cold forging. Steel is strong and does not bend easily, so it is used when you need tough parts.Design Complexity
If your design has tall fins or tricky shapes, cold forging lets you make more detailed parts. Extrusion is better for straight fins and simple shapes. If your design is very complex, extrusion may not work.Production Quantity
Think about how many heat sinks you need. Extrusion is best if you want to make a lot at once. Cold forging is better for small batches or special shapes.Cost Factors
The price of equipment and materials matters for your budget. Extrusion costs less to start and is faster. Cold forging costs more for each piece, but it can save money later if you want better cooling and higher performance.Thermal Management Requirements
If your device gets very hot or needs the best cooling, cold forging is the best choice. Extrusion is good for most electronics and gives you good cooling for less money.
Tip: Always pick your heat sink based on how much cooling you need, your budget, and how many you will make.
Here is a table to help you compare the main decision factors:
| Decision Factor | Cold Forging | Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Material Properties | Retains original structure, improves hardness | Material affects extrusion process |
| Design Complexity | Tighter tolerances, complex shapes | Limited by extruded geometry |
| Cost Efficiency | Efficient for high performance, higher unit cost | Lower initial cost, better for mass production |
| Production Methods | Best for lightweight, ductile metals | Continuous process, high output |
| Thermal Management | Excellent for demanding cooling | Good for standard applications |
Quick Selection Guide:
- Pick cold forging if you need high performance and tricky shapes.
- Choose extrusion if you want low cost and fast production.
- Extrusion saves money for big projects.
- Cold forging is better for important systems or high heat.
You can also check other heat sink types, like bonded, skived, stamped, or CNC machined. Each type works for different costs, airflow, and designs.
Checklist for Choosing:
What material do you want?
Is your design simple or complex?
How many will you make?
What is your budget?
How much cooling do you need?
You make the best choice when you match your heat sink to your project. Use this guide to help you decide fast and with confidence.
If you have a big project or normal electronics, pick Tran-Tec’s extrusion. Radian’s cold forging is better for powerful or important systems. Extrusion is good if you want things fast and to spend less money. Cold forging is better if you need more cooling and special shapes. Think about how much money you have, how well it needs to work, and how many you need. You can talk to suppliers or ask for samples to help you choose the best heat sink.
FAQ
What is the main difference between extrusion and cold forging heat sinks?
You get simple shapes and lower costs with extrusion. Cold forging gives you complex shapes and better cooling. If you want fast production, choose extrusion. If you need top performance, pick cold forging.
Which heat sink type cools better?
Cold forging heat sinks cool better. The process packs the metal tightly, so heat moves away faster. You should use cold forging for high-power devices or when you need the best cooling.
When should I choose an extruded heat sink?
You should pick extrusion for large orders, simple shapes, and lower costs. Extruded heat sinks work well in most electronics, like computers and home devices.
Is cold forging more expensive than extrusion?
Yes, cold forging usually costs more per unit. The process uses stronger tools and makes detailed shapes. You pay more, but you get better cooling and strength.
Can I customize both types of heat sinks?
You can customize both, but extrusion offers more flexibility for changes. Cold forging lets you make special shapes, but you need a new die for big changes.
Which process is faster for large orders?
Extrusion is faster for big batches. You can make more units per hour and get your order sooner. Cold forging works slower, so it fits smaller or special projects.
Are both types good for automotive or industrial use?
Both types work in cars and factories. Extrusion fits most needs and saves money. Cold forging gives you extra strength and cooling for tough jobs or high-power systems.
How do I decide which heat sink is right for my project?
Think about your budget, how much cooling you need, and how many units you want. If you want savings and speed, choose extrusion. If you need the best cooling and strength, go with cold forging.


