What Is a CPU Heat Sink
You count on your computer’s CPU to do every job, but all that hard work generates a lot of heat. Understanding what is a cpu heat sink is important because it sits directly on the processor and pulls heat away to keep it cool. If your computer does not stay cool, it can slow down or even suffer permanent damage. Heatsinks come in various shapes and sizes, and some are designed as custom heat sink solutions for unique or demanding requirements. Knowing about heatsinks and what a cpu heat sink does helps you keep your computer safe and running smoothly.
Key Takeaways
- A CPU heat sink helps cool your processor. It stops the processor from getting too hot. This keeps your computer working well.
- There are different types of heat sinks. Some are passive and some are active. Each type works best for certain cooling needs. They also fit different performance levels.
- Custom heat sinks are made for special systems. They help cool better and fit certain hardware.
- Good thermal interface materials help move heat from the CPU to the heat sink. This makes sure your computer works its best.
- You should check your heat sink often. Keep it clean and working right. This stops your computer from getting too hot. Overheating can cause problems and hurt your hardware.
What Is a CPU Heat Sink?

Definition and Function
You need to know what is a cpu heat sink if you want to keep your computer running safely. A CPU heat sink is a thermal management device that pulls heat away from your processor and releases it into the air. Engineers design heatsinks to protect your CPU from overheating by moving heat away quickly and efficiently. Most heatsinks use materials like aluminum or copper because these metals transfer heat well.
Tip: Always check that your heat sink sits flat on the CPU and uses thermal paste or a thermal pad. This step ensures the best contact and the most efficient heat transfer.
You will find that a typical heat sink has a wide base and many thin fins. These fins increase the surface area, which helps the heat escape faster. Some designs use fans to push air across the fins, making the cooling even better. Advanced heatsinks may include heat pipes or vapor chambers to move heat away from the CPU even faster. If you have a unique system or special cooling needs, you might need a custom heat sink. These custom solutions fit your hardware perfectly and handle higher heat loads.
Here is how a CPU heat sink works:
- It draws heat away from the CPU using a metal base.
- The heat spreads through the fins, which have a large surface area.
- Thermal paste or pads fill tiny gaps between the CPU and the heat sink for better contact.
- Fans can blow air across the fins to remove heat quickly.
- Some heatsinks use heat pipes or vapor chambers for advanced cooling.
Why CPUs Need Heat Sinks
Your CPU works hard and creates a lot of heat. Without a heat sink, the temperature can rise quickly and cause problems. Heatsinks keep your CPU cool and safe by giving the heat a way to escape. If you do not use a heat sink, your computer can slow down, crash, or even break forever.
Here are the main reasons you need a heat sink for your CPU:
- CPUs generate heat during every operation.
- Heatsinks absorb and spread this heat, preventing dangerous temperature spikes.
- Good heat management keeps your computer running fast and extends its life.
- Heat sinks with fins or pins release heat into the air more effectively.
- Custom heat sink options help when you have special hardware or higher cooling needs.
If you run your CPU without a heat sink, you risk serious problems. The table below shows what can happen:
| Risk/Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Overheating | The CPU temperature rises, which can cause damage. |
| Performance Degradation | The CPU slows down to protect itself from heat (thermal throttling). |
| Hardware Damage | High temperatures can permanently damage the CPU and other parts. |
| Safety Hazards | Extreme heat can cause electrical fires, risking safety and property. |
| Data Corruption | Sudden shutdowns from overheating can corrupt files and data. |
You should always use a heat sink that meets industry standards for safety and performance. For example, ISO9001 certification ensures that the heat sink was made with strict quality controls.
As CPUs get more powerful, they create even more heat in a small space. Heatsinks have evolved to keep up, using new materials and designs like vapor chambers and microchannels. If you have a high-performance system or a unique build, a custom heat sink can give you the cooling power you need.
How Heatsinks Work
Heat Transfer Science: Conduction, Convection, Radiation
You rely on heatsinks to keep your CPU cool, but how do they actually move heat away? Three main processes work together: conduction, convection, and radiation. Each plays a unique role in cooling your processor.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Conduction | Transfers heat through materials like copper or aluminum in the heat sink. |
| Convection | Uses airflow to carry heat away, with fans and fin design making a big difference. |
| Radiation | Releases heat from the surface of the heat sink into the surrounding air. |
Conduction starts the process. Heat travels from the CPU into the base of the heat sink. The choice of material matters here. Copper, with a thermal conductivity of about 398 W/m·K, moves heat faster than aluminum, which has a value around 235 W/m·K. This is why you often see copper in high-performance heatsinks.
Next, convection takes over. Air moves across the fins, carrying heat away. Fans boost this effect by increasing airflow. The design of the fins—how thick, tall, or spaced out they are—also affects how well the heat escapes.
Radiation plays a smaller part, but it still helps. The heat sink emits some energy as infrared waves, especially when the surface gets hot.
Key Components: Base, Fins, and TIM
A heat sink has three main parts that work together to keep your CPU safe:
- Base: This part sits directly on the CPU. It collects heat and spreads it out.
- Fins: Thin metal fins increase the surface area. More surface means more heat can escape into the air.
- Thermal Interface Material (TIM): This special paste or pad fills tiny gaps between the CPU and the base. It improves contact and helps heat move faster.
TIMs play a critical role. They fill microscopic air gaps that would otherwise slow down heat transfer. Good TIM application ensures your CPU stays cool and avoids thermal throttling. When you choose a custom heat sink, you get a solution designed for your exact needs, with the right materials and components for your system.
Tip: Always make sure the heat sink sits flat and the TIM covers the CPU evenly. This step gives you the best cooling results.
Types of CPU Heatsinks

Passive Heatsinks
Passive heatsinks work without fans or moving parts. They use conduction and convection to move heat away from the CPU. The heat goes from the CPU into the metal fins. Then, the heat escapes into the air. These heatsinks are good for small PCs and machines that need to be quiet. They are also used in places where reliability is very important.
Note: Passive heatsinks last a long time because nothing can break inside.
| Feature | Passive Heatsink | Active Heatsink |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Efficiency | Moderate; suits low-power CPUs | High; ideal for demanding CPUs |
| Noise Levels | None (silent) | Low to moderate (fan-dependent) |
| Power Consumption | Zero | Minimal (fan power) |
| Reliability | Very high (no moving parts) | Moderate (fan lifespan varies) |
| Cost | Typically lower, varies by size | Affordable to premium range |
Active Heatsinks
Active heatsinks use fans to blow air over the fins. This helps cool the CPU faster. You see these heatsinks in gaming computers and servers. Fans stop heat from building up. They keep your computer working well.
- Fans push air over the fins to cool the CPU.
- This makes heat leave faster and stops slowdowns.
- Active heatsinks help high-power CPUs stay cool.
Heat Pipe and Vapor Chamber Designs
Some heatsinks use heat pipes or vapor chambers. These have a special liquid inside. The liquid turns to vapor when it gets hot. Then, it turns back to liquid when it cools down. This moves heat quickly from the CPU to the fins.
- Heat pipes and vapor chambers use liquid that changes form.
- The vapor moves heat from hot to cool parts.
- Vapor chambers spread heat better than regular heat pipes.
These designs are used in powerful computers and small spaces.
Custom Heat Sink Solutions
Custom heat sinks are made for special needs. You need them when regular heatsinks do not fit. They are used in data centers, factories, and airplanes. These places need special shapes or materials.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Centers | Many CPUs run all day and need strong cooling. |
| Industrial Applications | Tough places need heatsinks that work well and last long. |
| Aerospace Applications | Heatsinks must handle high heat and shaking, and follow strict rules. |
Custom heat sinks give the best fit and cooling for hard jobs. If you want to know what is a cpu heat sink for tough needs, custom ones are best.
Materials and Performance in Heatsinks
Copper vs. Aluminum
Copper and aluminum are common in heatsinks. Each has its own benefits. Copper moves heat away from the CPU very fast. Aluminum is lighter and costs less money. You should think about your cooling needs and budget before you choose.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | ~400 | Excellent Performance |
| Aluminum | ~235 | Lightweight & Lower Cost |
| Stainless Steel | ~16 | High Corrosion Resistance |
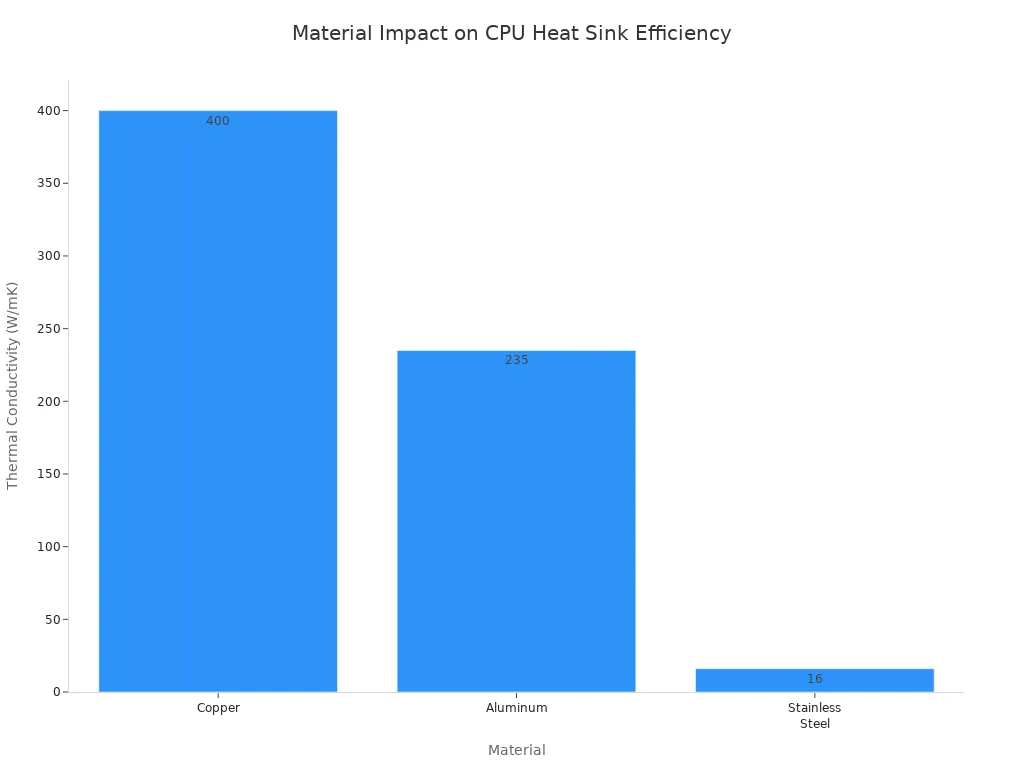
Copper is best for high-performance computers. Aluminum works well for lighter or cheaper builds.
Hybrid and Advanced Materials
Hybrid and advanced materials can cool even better. Engineers mix materials to get more benefits. Hybrid heat sinks use phase change materials with special fins or nanoparticles. These designs help spread heat quickly and keep CPUs cool.
- Foam fins make the heat sink lighter and hold more PCM.
- Hybrid active–passive systems handle high heat better.
- Custom fin shapes and vapor chambers move heat in small devices.
- Aluminum-graphite composites send heat where it is needed most.
You find these advanced materials in custom heat sinks for data centers, factories, and small electronics.
Impact on Cooling Efficiency
The material you pick changes how well your heat sink cools. Copper and aluminum both work well, but you need to look at your whole system. Using the wrong material can cause overheating or failure. High-conductivity materials like copper and aluminum stop heat from building up and help your CPU work well.
Design matters too. Wider fin spacing and thicker base plates spread heat better, especially in passive cooling. When you ask what is a cpu heat sink, remember that the right material and design keep your computer safe.
Tip: Always match your heat sink’s material and design to your system’s needs for the best results.
What Makes a Custom Heat Sink Special?
Unique Designs and Tailored Fit
You might ask why a custom heat sink is different. The main reason is its special design and perfect fit. Custom heat sinks can have microchannels for tight spaces. Some use 3D printing to make cool shapes. Others have vapor chambers for strong CPUs. Composite materials help with special heat problems.
| Technology | Best Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Microchannel | High-density electronics | Superior liquid cooling efficiency |
| 3D Printed | Custom, complex applications | Unmatched design freedom |
| Vapor Chamber | High-power CPUs/GPUs | Excellent heat spreading |
| Composites | Specialized thermal paths | Tunable thermal properties |
A custom heat sink fits your device just right. Engineers make it the exact size and shape you need. This helps the heat sink work better. The fins and surface are made to move heat away fast. Your computer stays cooler and works longer. Heat leaves faster, so your parts last more years.
Performance and Aesthetic Benefits
Custom heat sinks do more than cool your CPU. Tests show top models like the Noctua NH-D15 G2 and DeepCool Assassin IV work very well. They are easy to put in and have strong mounting parts.
| Cooler Model | Performance Rank | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Noctua NH-D15 G2 | 1 | Impressive mounting, tuning |
| DeepCool Assassin IV | 2 | Ease of use, installation |
| NH-P1 | 3 | Excellence in passive cooling |
| Sudokoo SK700 | Middle | Sturdy build, high fin density |
Custom heat sinks can also make your PC look cool. You can pick ones with shiny tubes, RGB lights, or fun shapes. Many people want their computer to look special. Custom cooling gives you both good looks and great performance. Your system will run well and stand out.
When to Choose a Custom Heat Sink
Pick a custom heat sink if you need extra cooling or a perfect fit. These are best for gaming, work computers, and big servers. You want to stop your CPU from slowing down and keep it safe.
| Situation | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Performance Gaming | Prevents thermal throttling during long sessions, keeps performance stable |
| Workstation Builds | Maintains optimal temperatures for video editing and 3D rendering |
| Enterprise Servers and Data Centers | Ensures uptime and reliability, prevents overheating failures |
Custom heat sinks cost more than regular ones. You pay for better stuff, cool shapes, and new ways to make them. If you want the best cooling and a cool look, a custom heat sink is a good choice.
You now know what a cpu heat sink does. It helps keep your computer safe and fast. Heatsinks use special shapes and materials to move heat away. You can pick passive, active, or custom heat sinks. The type depends on what your computer needs. When you choose a heatsink, think about these things: how much heat your system makes, how strong it needs to be, how easy it is to put together, how your PCB is built, and how much money you want to spend. Picking the right heatsink keeps your computer cool and working well.
FAQ
You use a CPU heat sink to move heat away from your processor. This keeps your computer cool and prevents damage. A good heat sink helps your system run smoothly and last longer.
You need a custom heat sink if your system has special size, shape, or cooling requirements. High-performance computers, servers, or unique builds often require custom solutions for the best results.
You should not install a heat sink without thermal paste. The paste fills tiny gaps between the CPU and the heat sink. This improves heat transfer and keeps your CPU safe.
You should replace thermal paste every two to three years. If you notice higher temperatures or remove the heat sink, apply new paste for the best cooling.
Custom heat sinks can improve performance. They keep your CPU cooler, which prevents slowdowns and extends hardware life. You get better results, especially in demanding tasks.



